
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

In today’s dynamic mobile app development landscape, the right programming language powered by the appropriate integrated development environment (IDE) is key to building a robust mobile solution. This article illuminates the fundamentals of Android app development and its IDEs, identifies the top Android programming languages, reviews their pros and cons, and explains how to choose the right programming language for a flawless Android app development process.
Android app development is a software engineering process centered on creating apps for touchscreen devices—smartphones and tablets—that run on the Android mobile operating system (OS). Developing for the Android OS requires using programming languages, which can be broadly categorized into native and cross-platform, and their related IDEs. In addition to providing necessary development, testing, and debugging tools and facilitating the software development process, the right IDE also substantially increases productivity and drives efficiency. Considering the importance of IDEs for both the development process and the understanding of how a programming language is used, let’s briefly outline the best IDEs for Android apps. Android app development IDEs include but are not limited to the following.
Android Studio is an official IDE for Android app-building, containing a software development kit (SDK) that enables developers to write native mobile apps specifically for the Android OS. It supports the Java and Kotlin official Android programming languages and is a unified space to build software solutions for all Android-based devices. This IDE offers a wide range of powerful instruments, including JetPack Compose, an intelligent code editor and Live Edit, the Gradle-based build system, the Android Emulator, and more.
The Visual Studio IDE by Microsoft integrates with the Xamarin framework, allowing developers to create cross-platform mobile apps with the C# programming language by sharing the same codebase across several operating systems, including Android, iOS, and Windows. Providing a comprehensive set of development tools and access to platform-specific application programming interfaces (APIs), Xamarin facilitates the development of full-fledged Android apps delivering native-like user experience (UX).
Although Visual Studio Code is a source-code editor, many developers use it as a powerful IDE to write apps for the Android, iOS, and Windows platforms. The source-code editor supports the Flutter and React Native frameworks, enabling cross-platform mobile app development with the Dart and JavaScript programming languages, respectively. By leveraging Flutter and React Native, developers share code across various operating systems and deliver efficient mobile solutions with near-native functionality and performance.

Now that you are equipped with knowledge about Android IDEs, let’s delve into the related programming languages utilized to build native and cross-platform Android mobile solutions.
Android software developers capitalize on the following languages to write native apps:
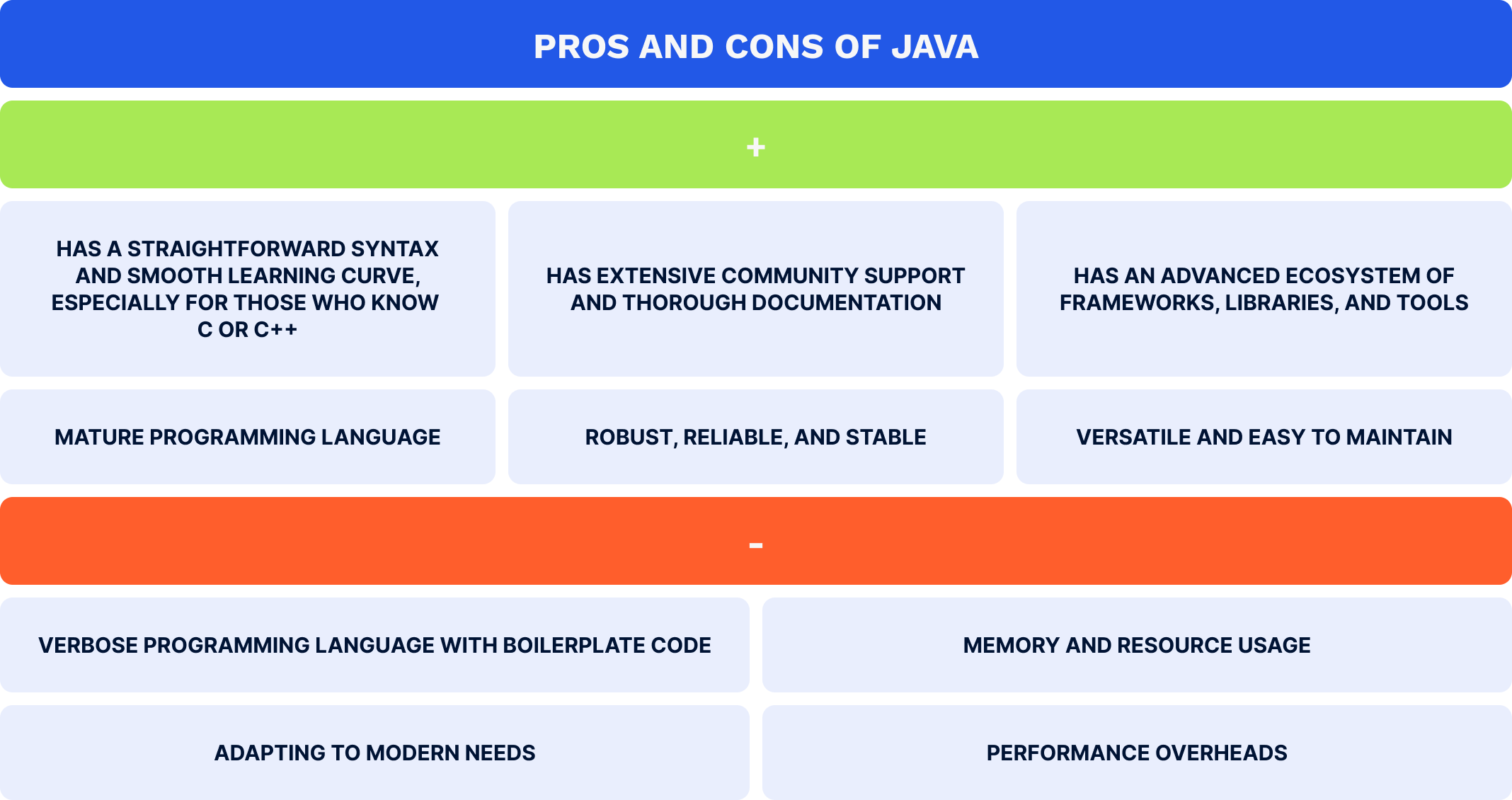
Java is an open-source, high-level programming language with object-oriented programming (OOP) features, and it follows the “write once, run anywhere” (WORA) concept. This means that Java code is written for one platform, but it then compiles into a bytecode file that runs across multiple operating systems with the help of a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Developers use this general-purpose language to build back ends for solutions of any complexity, be it a web app or enterprise-level software. Dubbed as the first official language for Android app development, Java is an efficient tool to create robust mobile solutions. Some software developers still consider Java the best Android development language, although Kotlin is overtaking it in popularity. Here is an overview of the pros and cons of Java:
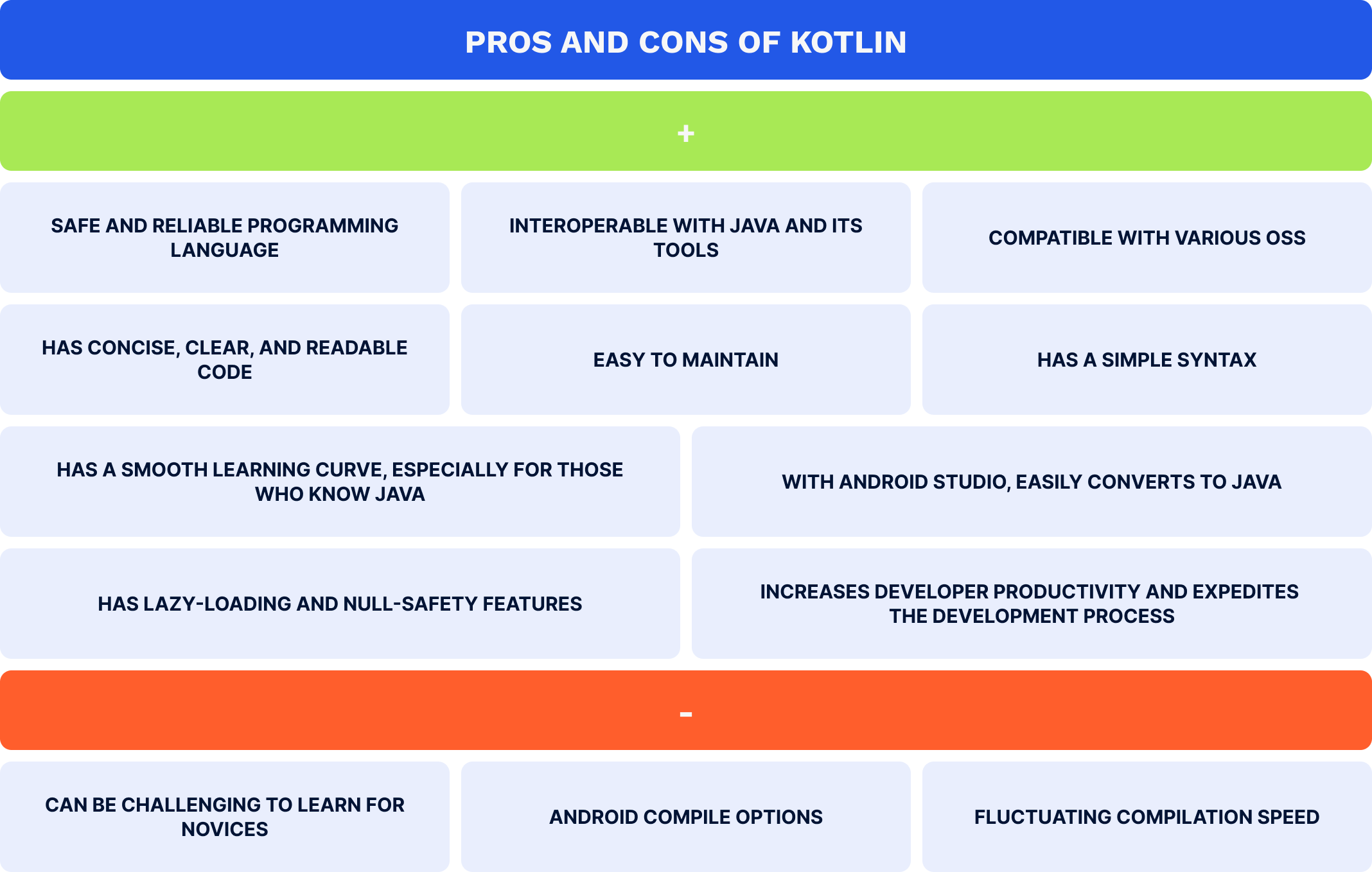
Kotlin, another official programming language for Android app development, is the number one choice of developers for crafting state-of-the-art native Android apps, with more than 50% of Android developers using it as their primary programming language. As a modern, open-source language with OOP and functional programming capabilities, Kotlin is used for various purposes, including server-side, client-side, and full-stack web and Android mobile app development. This language is fully interoperable with Java, generates code that runs on a JVM, and supports Java frameworks, libraries, and tools. When used for Android mobile app development, Kotlin offers all the advantages of the Java programming language and opens up multiple opportunities due to its powerful features, including lazy loading, which reduces the startup time of Android apps, and null safety, which helps bypass Android apps’ runtime crashes. Following are Kotlin’s advantages and disadvantages:
 Now that you are familiar with two official programming languages for Android app development, let’s explore which cross-platform languages empower building apps for the Android OS:
Now that you are familiar with two official programming languages for Android app development, let’s explore which cross-platform languages empower building apps for the Android OS:
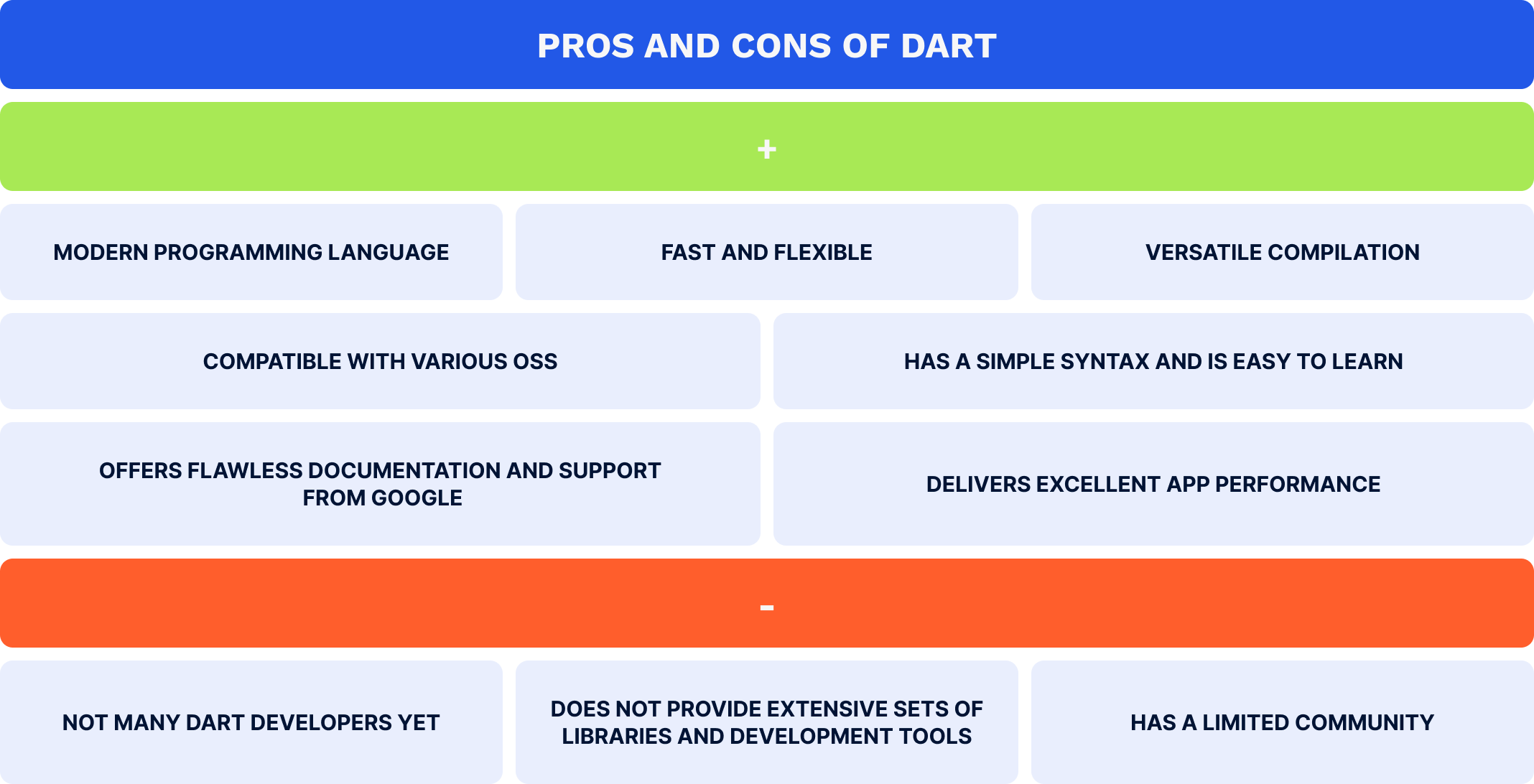
Dart is an open-source, OOP language developed by Google, used for building front-end systems for web, desktop, and mobile apps. It is a particularly powerful Android app programming language that covers cross-platform mobile app development needs if combined with the Flutter framework. Dart and Flutter offer an excellent variety of important features, such as hot reloading, which enables developers to edit code and view changes in real time, resulting in faster iterations and more streamlined development and debugging processes. By leveraging Dart with Flutter’s rendering engine, Impeller, developers build visually appealing, interactive, and customizable user interfaces (UIs). In addition, Dart supports both just-in-time (JIT) compilation, responsible for improving speed and application runtime, and ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation, which aids in optimizing app performance and identifying mistakes. Dart’s trade-offs are as follows:
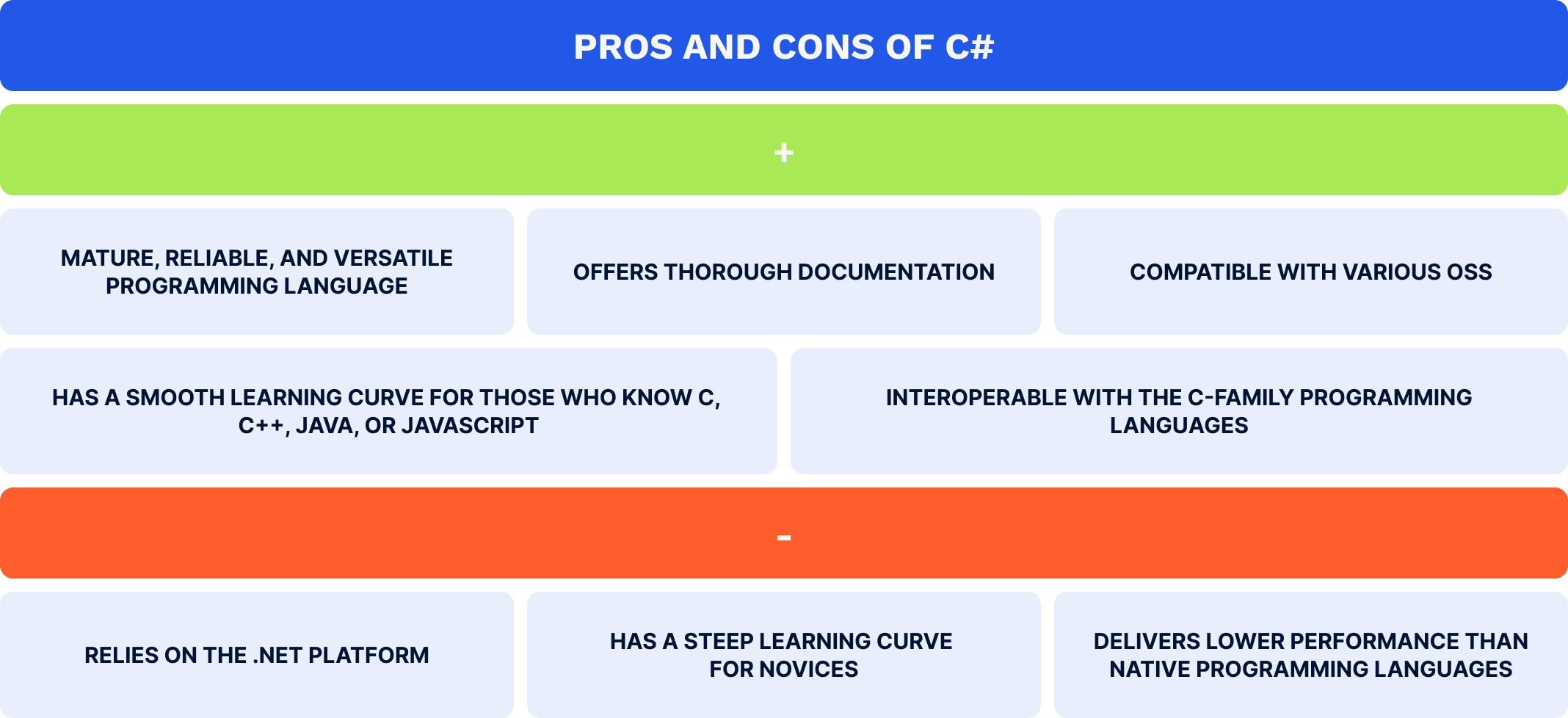
C# is an open-source, object-oriented, and type-safe programming language that was created by Microsoft to build Windows apps in combination with the .NET Framework. Developers take advantage of this high-level programming language not only to build back-end systems for games, databases, and web and desktop software but also to write cross-platform mobile apps for the Android and iOS operating systems. However, in this case, using the Xamarin or .NET MAUI frameworks is necessary. By utilizing C# as an Android coding language, along with Xamarin or .NET MAUI, software engineers can easily develop robust Android and iOS mobile apps that deliver seamless performance, maintain multiple native features, and provide frictionless UX. Leveraging C# as a primary language for Android app development has the following benefits and drawbacks:
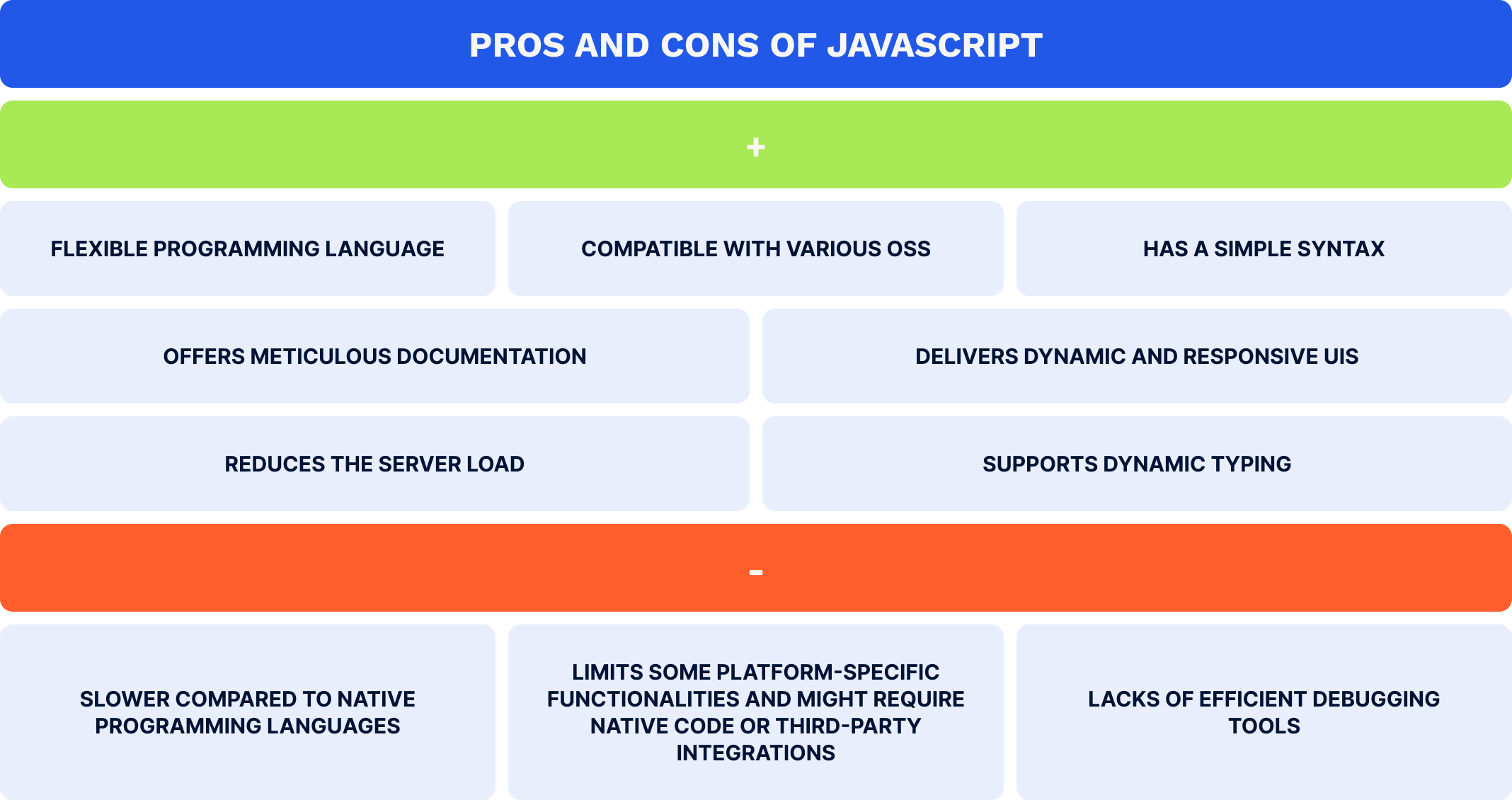
JavaScript is a high-level, OOP language primarily used in front-end development to create highly dynamic and interactive content for websites, web pages, and online games. However, integrating open-source JavaScript with the React Native framework creates an ideal combination for building cross-platform Android and iOS mobile apps. JavaScript’s versatility with React Native’s component-based architecture allows developers to build reusable UI components and render complex UIs with advanced animations and sophisticated graphics, elevating UX and increasing business visibility. Furthermore, JavaScript and React Native’s features, such as hot reloading and code reusability, significantly facilitate and expedite the development process while delivering native-like app performance. Below are the advantages and disadvantages of JavaScript as a language used for Android app development:
Before deciding on the best programming language for Android app development and selecting a corresponding tech stack, companies should consider several essential factors, including the purpose of their mobile app, the features implemented, their target market, their budget available, and more. After considering all these elements, business stakeholders can opt for native Android app development with Java and Kotlin if they prioritize:
On the other hand, capitalizing on C#, Dart, and JavaScript for cross-platform mobile app development is an optimal choice if businesses want to ensure:
Any of the above-mentioned native and cross-platform programming languages offers compelling benefits that can help streamline the development process and address business challenges.
“Mobile app development for various operating systems, including Android, has significantly evolved since its inception. Not only have the primary Java and Objective-C programming languages progressed immensely over time but new programming languages have also emerged, dramatically enhancing the speed and efficiency of the development process. IDEs for Android have considerably advanced as well, leading to streamlined workflows and an accelerated development process. The shift from the Eclipse IDE, leveraged as an adaptation for mobile development, toward a powerful Android Studio tool has gained widespread developers’ support, resulting in the latter becoming a one-size-fits-all IDE for developers.” – Eugene Baldovsky, Head of Mobile.

Determining the best language for Android app development is a daunting but not impossible task that can make or break UX with a mobile app. While Java and Kotlin empower native Android app development, C#, Dart, and JavaScript require the use of their corresponding frameworks to ensure a smooth cross-platform development process for the Android and iOS operating systems. If you are searching for a reliable one-stop app development partner to adeptly craft a robust Android mobile solution, our team of expert developers is available to help. Contact us now!
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659