Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
The days of legacy systems and brick–and–mortar banking are gone. Thanks to the emergence of cloud banking, the financial sector has undergone a remarkable transformation. What started as an experimental concept, has now become one of the driving forces in modern finance. Cloud banking has not only simplified digitalization in the banking industry, but also streamlined innovation, efficiency, and customer-centricity. It has revolutionized the way banks operate, driving progress and enabling a seamless banking experience. Want to learn more? Keep reading!
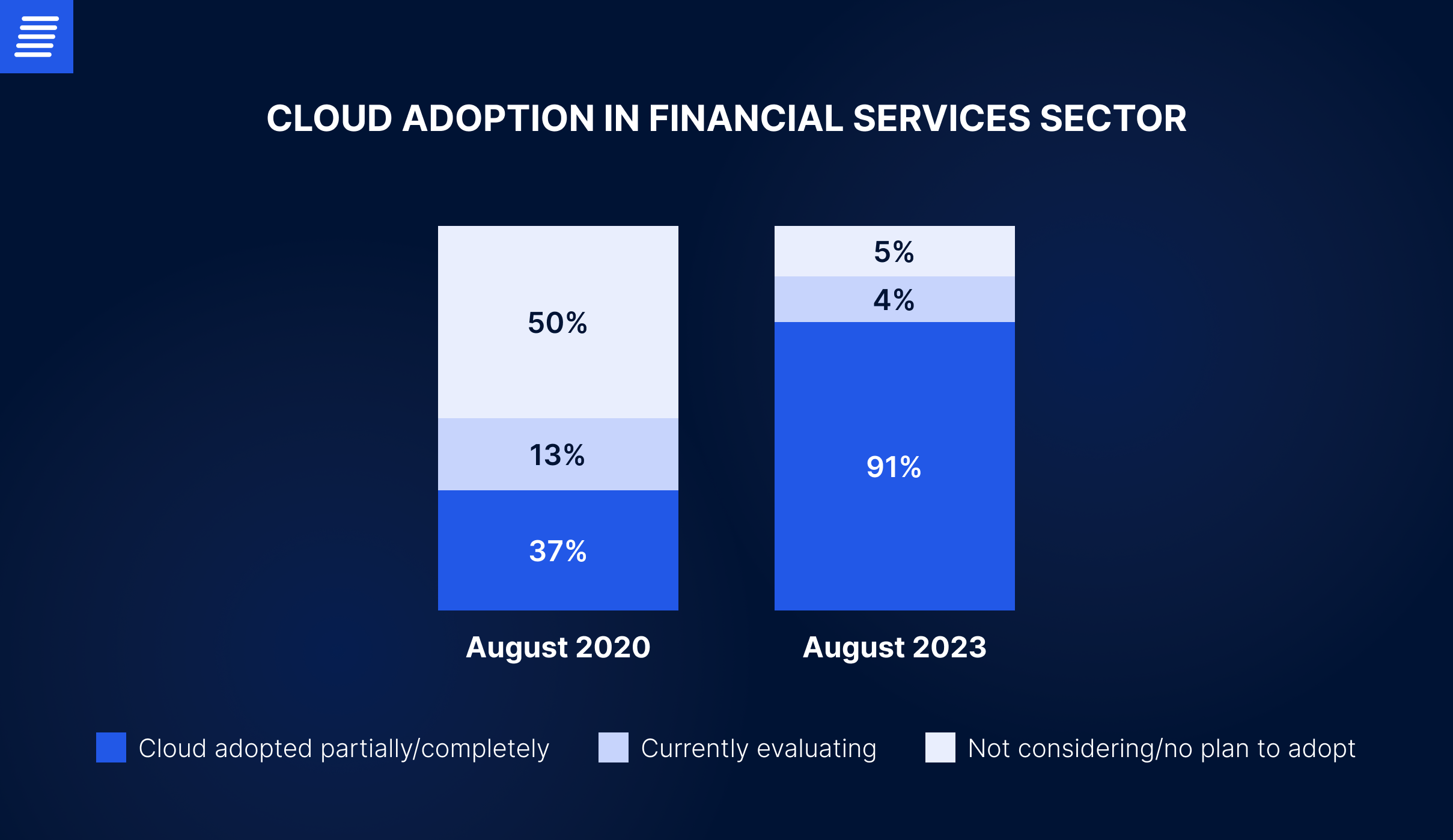
In this era of ongoing technological changes, tougher competition, and soaring customer expectations, the banking industry is under constant pressure. Cloud computing emerged as a key strategy to address this pressure, allowing members of the banking sector to rapidly embrace innovation and adapt to market dynamics. According to the World Cloud Report 2023 on financial services, the banking and insurance industries have accelerated cloud adoption initiatives in recent years. The percentage of companies embracing cloud computing rose from 37% in August 2020 to 91% in August 2023.
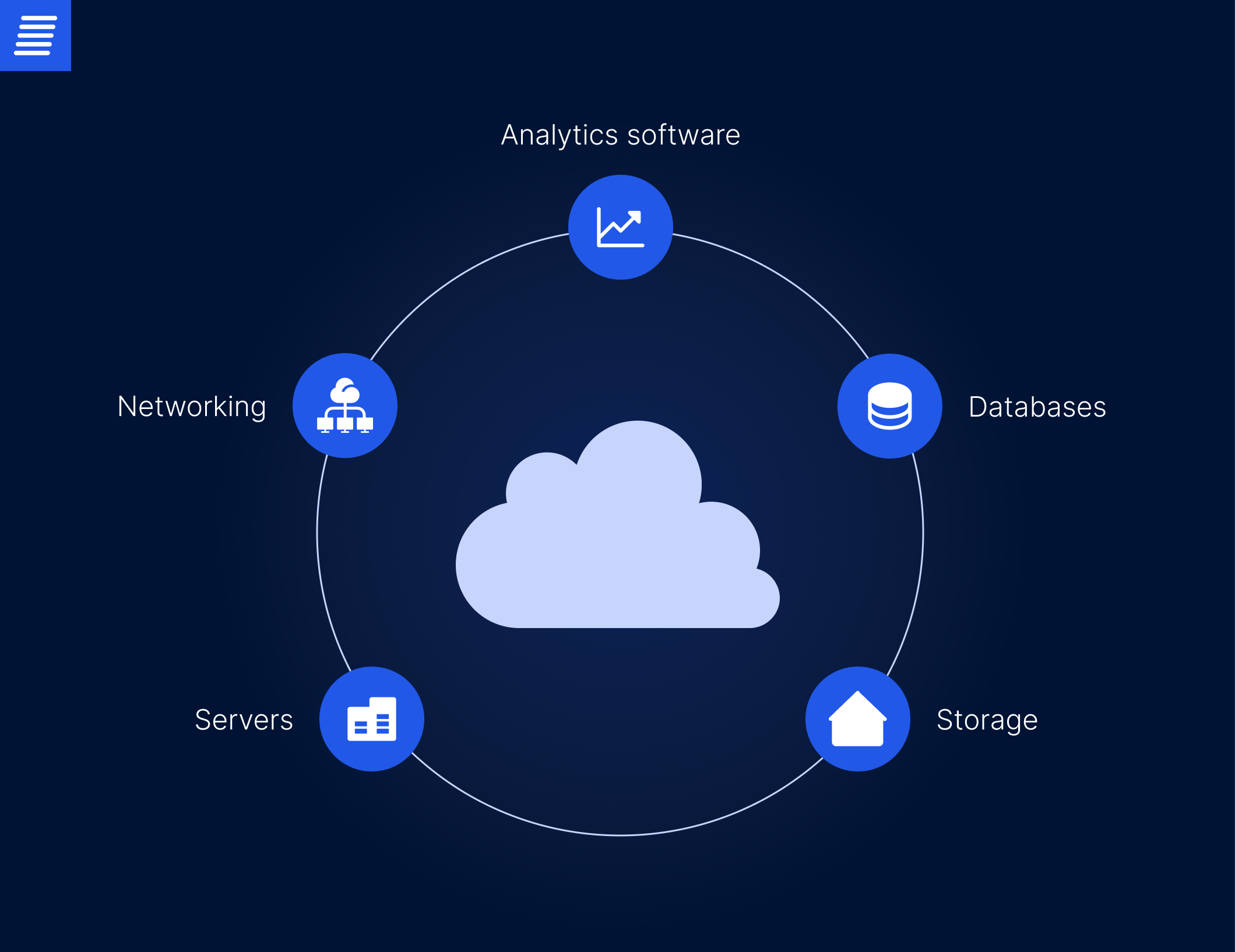
In the spectrum of modern financial services, cloud computing has navigated the transition from the complexity of traditional IT infrastructure to today’s flexibility and scalability. Freed from old-school computers and cumbersome servers, which were not only expensive but also required extensive maintenance, banking operations have become faster and smarter. Today, all the complex data and transactions are conducted in the cloud – a virtual environment where banks can leverage the necessary computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, networking, and analytics software for storing, managing, or processing data without being required to own them.
When it comes to adopting cloud services, banks have unique considerations. The choice of the model is influenced by factors such as cost, compliance, security, and operational needs. Below are the primary cloud environments banks can choose from:
Banks can tap into resources provided by third-party cloud service providers via the Internet. These services are shared with other organizations and are ideal for non-sensitive operations, offering cost efficiency, high scalability, and a broad selection of services that reduce the need for substantial investments.
For operations that involve sensitive data or require more stringent control and security, banks can use a private cloud. This can be hosted internally (on the bank’s premises) or externally by third-party providers, but it remains exclusively for the bank’s use. The main benefit of a private cloud is enhanced security and the ability to tailor resources to specific banking workflows.
To optimize flexibility, banks can employ a hybrid cloud strategy. This involves integrating public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move seamlessly between the two environments. This model is particularly advantageous for balancing agility, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
In specific scenarios, community clouds offer collaborative infrastructure shared between several organizations with common concerns (such as security, compliance, and performance requirements). This is particularly beneficial for smaller banks or financial institutions that require specialized services but want to share costs.
Cloud banking services are offered under various models, each designed to align with different aspects of the banking infrastructure:
This is the foundational layer of cloud services, where banks can rent computing power and storage on-demand, eliminating the capital expense and maintenance requirements associated with hardware ownership. IaaS provides banks with the raw materials of IT infrastructure, offering flexibility and scalability as they grow or face fluctuating demand.
PaaS takes things a step further by providing banks with a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud. This includes tools for building, testing, and deploying banking applications quickly and efficiently. This option is ideal for banks looking to develop new services or apps without the overhead of building and maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
In the SaaS model, banks access applications hosted by service providers over the Internet. This eliminates the need for installing and running these applications on individual bank computers, simplifying maintenance and support. SaaS solutions are typically subscription-based and can range from core banking systems to customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
By capitalizing on these cloud computing models and services, banks are not only able to modernize their IT environment but also align their operations with the harsh demands of the finance sector.
Identifying the optimal cloud computing model for financial services hinges on a comprehensive analysis of the institution’s strategic objectives, regulatory obligations, and risk tolerance. Following are the primary steps in this process.

Banks must align their cloud strategy with their business goals, whether they aim to increase agility, reduce costs, or drive innovation.
When selecting a cloud model, it is essential to consider the regulatory environment to ensure that the provider’s services enable compliance.
Understanding the risk profile and effectively managing the risks associated with data security, privacy, and operational resilience is critical.
A hybrid cloud model is often the preferred choice in the banking industry, blending the enhanced control and security of the private cloud with the cost efficiencies and scalability of the public cloud.
Cloud computing offers a wide array of benefits. In this section we will highlight the benefits most likely to drive the decision to embrace cloud banking.
For banks, cloud computing represents a new approach to cost management due to an operational expenditure (OPEX) model rather than a capital expenditure (CAPEX) model. By leveraging the resources of third-party providers, financial institutions can avoid the large upfront costs associated with owning and maintaining data centers. Instead, banks pay for cloud services on an as-needed basis, scaling up or down to match real-time demands. Cloud computing also reduces expenses from underutilized on-premises resources, establishing a direct alignment between costs and business.
Cloud banking enables the rapid allocation of computing resources, facilitating quick responses to spikes in demand. Cloud infrastructure can scale elastically to support fluctuating workloads with the flexibility to expand services or storage without being constrained by insufficient physical resources. Banks can also scale down resources when not needed, optimizing costs and achieving a level of agility difficult to attain with on-premises systems.
Contrary to common misconceptions about cloud vulnerability, leading cloud providers implement complex security practices that are beyond the reach of individual companies. These include robust access controls, data encryption, network security, application-level controls, and advanced threat detection. Cloud providers also undertake rigorous compliance audits and penetration testing. By leveraging the cloud, banks reduce their internal security burden while benefiting from state-of-the-art protection.
For banks, the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing are critical assets in creating an environment of continuous innovation. By leveraging cloud services, banks can dynamically allocate resources to develop and launch new digital banking products. This agility facilitates the rapid prototyping and testing of proofs-of-concept, allowing banks to refine their offerings in direct response to real-time customer feedback. This iterative approach to product development, supported by the cloud, accelerates the deployment of enhanced services.
Cloud computing enhances a bank’s business continuity and disaster recovery capabilities by dispersing data across multiple geographically diverse data centers. This ensures that local events won’t disrupt operations, thereby guaranteeing continuous service availability. Cloud providers also offer built-in redundancy for critical systems, minimizing downtime. By leveraging the cloud, banks can provide reliable access to banking services, reinforcing their reputation for stability.
Cloud computing helps banks achieve regulatory compliance. Cloud providers offer robust data protection measures required for compliance with regulations like GDPR and banking standards. Audits and reporting tools can be used verify adherence to regulations. Cloud security policies and infrastructure design frequently align with major compliance frameworks, facilitating certification processes that are mandatory in the domain.
While the benefits of cloud computing may strongly influence cloud adoption, banks need to equally evaluate the risks and challenges involved. Understanding these potential pitfalls is key to creating an effective cloud migration and implementation strategy. With the right approach and a carefully selected software service provider, banks can minimize the downsides of moving to the cloud while maximizing its many upsides.
This section dives deeper into the key challenges and risks financial institutions must consider when transitioning core functions to the cloud.
Many banks operate on legacy systems that are entrenched in their daily operations. Integrating these systems with modern cloud solutions can be a complex task that requires careful planning and execution. Banks must address issues of compatibility, data migration, and service continuity to create a seamless integration that leverages the benefits of the cloud without disrupting ongoing operations.
Reliance on a single cloud provider can lead to vendor lock-in, making it difficult and expensive for banks to switch providers in the future. This can limit banks’ negotiating power and flexibility, and potentially impact service continuity. Banks should carefully consider adopting a cloud-agnostic strategy that prevents over-reliance on a single vendor. This can be achieved by architecting via open standards like OpenAPI and implementing planning to mitigate risks.
Migrating data to the cloud is a significant undertaking, especially for banks that have accumulated vast amounts of data over decades. Ensuring data integrity, managing the transition without disrupting services, and addressing the technical challenges of moving large datasets are key concerns. Additionally, banks must decide which data to move to the cloud and which to keep on-premises, which often requires a detailed analysis of data sensitivity, usage patterns, and cost implications.
The performance of cloud-based applications can be affected by latency issues, particularly when cloud data centers are located far from end-users. Banks need to ensure that their cloud architecture is designed to minimize latency for critical applications, especially those requiring real-time processing such as transaction systems. Utilizing a combination of edge computing, distributed caching, predictive scaling, and advanced traffic monitoring tools for traffic management can help create solutions that deliver low latency and consistent performance.
Banks often adopt multi-cloud or hybrid strategies encompassing both public cloud platforms and internal private cloud or legacy systems. In these cases, ensuring seamless interoperability between two environments is paramount, making connectivity and data exchange across platforms a top architecture-related priority.
An effective strategy involves implementing loose coupling through APIs and abstraction layers. Utilizing CI/CD pipelines combined with extensive testing allows changes to be deployed frequently without disrupting interoperability.
Maintaining governance and control over IT resources in a cloud environment can be challenging. Banks must establish clear policies and procedures to manage cloud resources, ensure proper oversight, and maintain compliance with internal and external policies. To further enhance governance, banks should implement cloud management platforms and DevSecOps toolchains to provide centralized control, automation, and continuous compliance across hybrid cloud environments.
While cloud providers typically offer robust security features, the dynamic nature of the cloud and its broad accessibility can introduce new vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors. Banks must stay vigilant against emerging cybersecurity threats and continuously update their security practices to protect customer data and maintain the integrity of their financial services. Furthermore, adopting a zero-trust approach enhanced by analytics-driven threat detection and automated response capabilities allows banks to proactively strengthen defenses across their cloud ecosystem.
Although the adoption of the cloud in the banking industry is complex and comes with challenges, banks can navigate this process successfully by keeping the above considerations in mind and partnering with a knowledgeable software service provider. This approach can pave the way for a cloud-enabled ecosystem that is secure, compliant, and optimized for the digital age.
Cloud computing is revolutionizing the banking industry through a wide range of scenarios, including the following use cases:
Cloud platforms provide a robust foundation for core banking systems, offering the flexibility to handle fluctuating workloads and the ability to scale resources on demand. Enhanced scalability and reliability are critical for processing high volumes of transactions and managing customer data. Moreover, cloud environments can reduce operational costs due to their pay-as-you-go pricing models. However, the migration of core systems requires careful planning to ensure data security, system compatibility, and minimal service disruption.
The adoption of cloud-based digital payment solutions is pivotal in meeting the growing customer demand for convenient, cashless transaction options. Cloud infrastructure enables rapid development and deployment cycles, allowing banks to quickly innovate and adapt payment solutions in response to emerging trends and technologies. This agility is crucial in an industry where payment modalities are evolving rapidly.
Cloud computing’s capacity for handling vast datasets enables the deployment of sophisticated fraud detection and security systems. Utilizing advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI, banks can identify and respond to suspicious activities in real-time, significantly enhancing their defensive posture. The scalability of the cloud facilitates the processing of large-scale data analysis required for these tasks, although ensuring the privacy and security of this data remains a top priority.
Cloud-based CRM systems offer banks the ability to integrate data from various touchpoints, providing a 360-degree view of the customer. This integration enables personalized service offerings and can significantly improve customer satisfaction and retention. The cloud’s scalability also allows for the efficient handling of CRM system expansions as the customer base grows.
By utilizing cloud platforms, banks can leverage powerful analytics and business intelligence tools for processing and analyzing data, gaining valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and internal operations. These insights can inform strategic decisions and drive competitive advantages. The flexibility of the cloud supports the dynamic nature of analytics workloads, which can vary greatly in resource requirements.
The BaaS model is an innovative approach enabled by cloud technology, allowing banks to extend their infrastructure and banking services to third parties. This collaboration can spur the development of new financial products and services, driving additional revenue streams and fostering innovation in the financial sector. However, it also introduces complexities in terms of partnerships, service level agreements, and API management.
Successful implementation of these use cases by leading experts in cloud banking software services enables banking companies to benefit from the technical advantages of the cloud while avoiding the associated regulatory, security, and operational challenges. With a reliable software development partner, the cloud can serve as a key enabler for innovation and efficiency in the banking sector.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the banking industry, enabling agility, efficiency, and innovation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Financial institutions that embrace this transformation are better equipped to meet market demands, embrace technological advancements, and deliver value to customers and stakeholders. To embark on this transformative journey or optimize existing cloud strategies, professional guidance is essential. Partnering with experts in software development services for the banking sector ensures a smooth, secure, and strategic move to the cloud.
The digital race is on—don’t be left behind! Contact us today to explore how our specialized banking software development services can empower your bank with the cloud solutions you need to thrive in the modern financial ecosystem.

Banks must adhere to a variety of compliance requirements, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) in the U.S., and global standards like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Though challenging, banks can integrate legacy systems with cloud solutions through APIs, middleware, or by using a phased migration strategy to modernize their IT infrastructure.
Risks include data breaches, service outages, and compliance violations. However, through careful planning, risk assessments, and the selection of the right cloud provider, banks can mitigate these risks.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form to receive a consultation and explore how we can assist you and your business.
What happens next?