Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

The manufacturing sector is at the forefront of economic growth and innovation and has witnessed a plethora of transformations over the years. Today, it continues to evolve in leaps and bounds as the process of digital transformation is currently gaining traction. What does this process particularly involve? In this article, we take a comprehensive look at what digital manufacturing entails and focus on the current tech trends, benefits, challenges, and practical examples of the same.
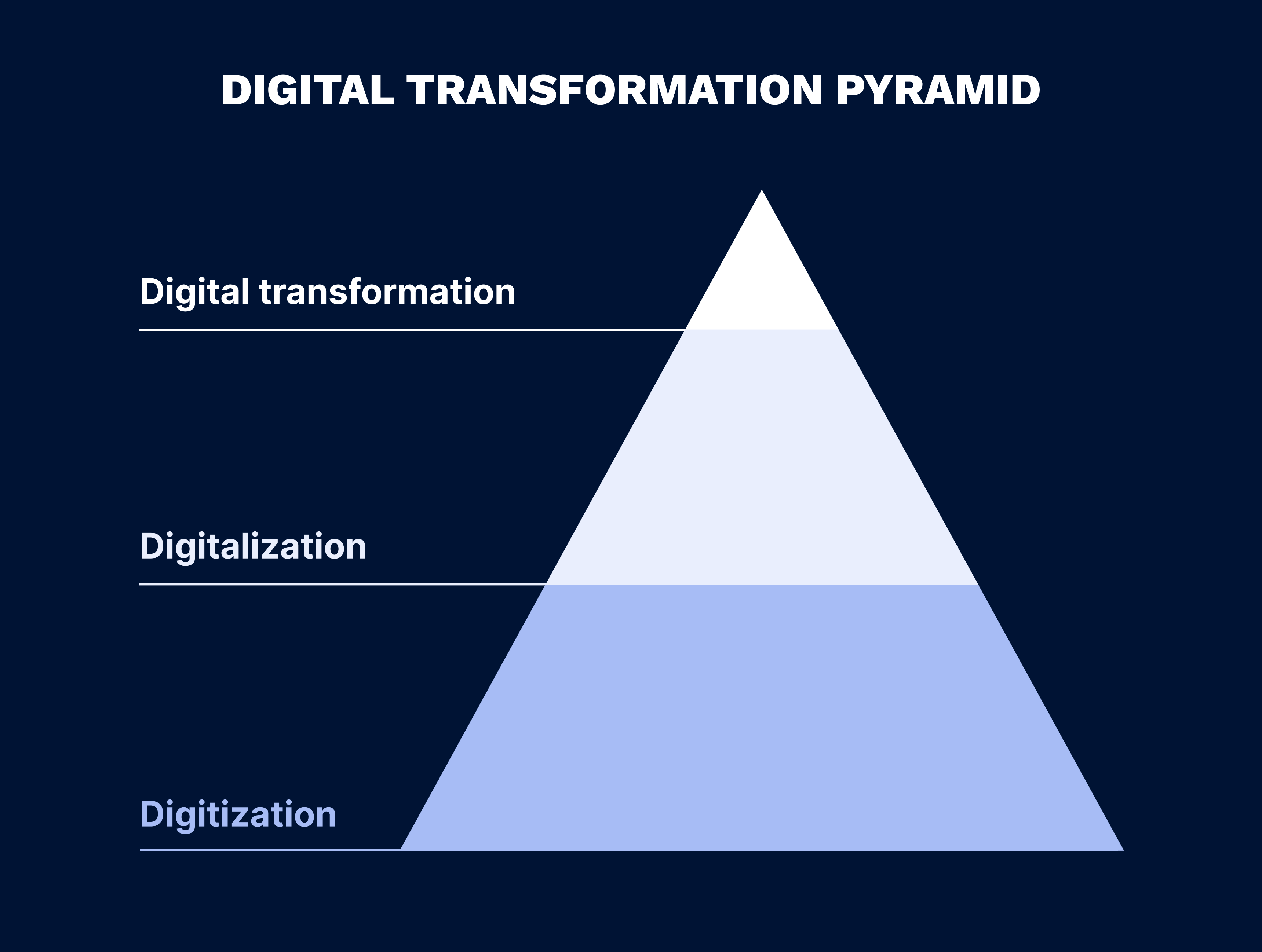
According to McKinsey & Company, “digital transformation is the rewiring of an organization, with the goal of creating value by continuously deploying tech at scale”. In essence, digital transformation (DX) is a strategy that involves the integration of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), and augmented reality (AR), into all aspects of a business. The goal of DX is to completely change how a company operates, improving its operational efficiency, supporting employees, and driving value to customers. DX is often confused with digitization and digitalization, both of which, however, are the predecessors of DX:
DX builds upon these concepts and involves the transformation of business models, strategies, and goals, cultivating a digital culture for increased productivity and improved customer engagement.
Manufacturers seek to adopt digital technologies to enhance their performance and agility, improve product quality, remain competitive in the market, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction. However, to achieve these goals, manufacturing companies should as well review their internal business processes and significantly improve their corporate culture by enabling employees to embrace digital solutions.
The increasing integration of powerful technologies into manufacturing, including big data, industrial internet of things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and robotics, has given rise to Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution. The use of advanced technologies to enhance production processes has powered the development of smart manufacturing, the principles of which underpin the creation of smart factories.
Smart factories are cyber-physical systems (CPS) capable of integrating hardware and software components to interact with the physical world and efficiently complete well-defined tasks in real-time. They facilitate collaboration between various production departments, boost productivity, and increase manufacturers’ overall profitability.
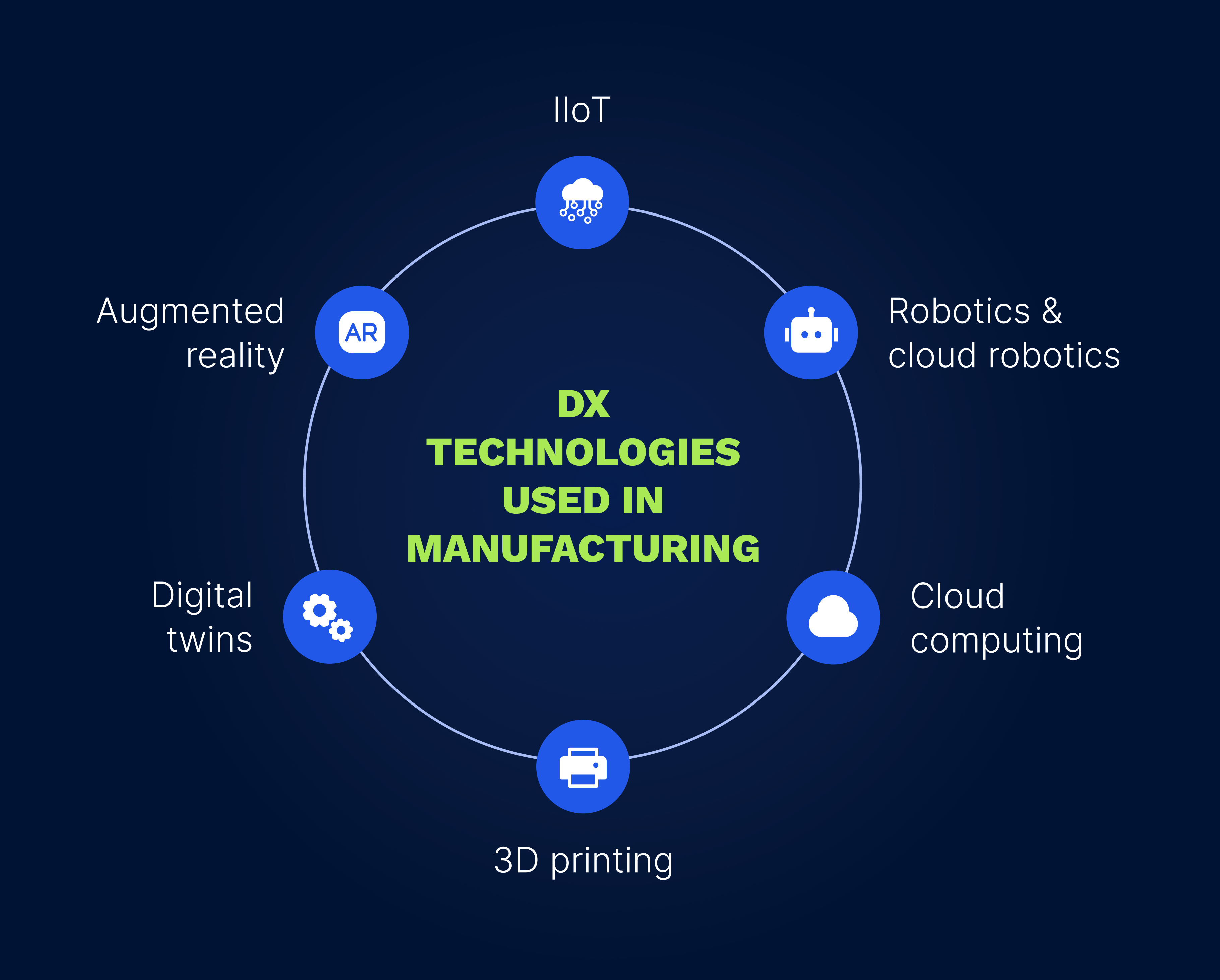
To ensure successful digital transformation in the manufacturing industry, leveraging the power of these intelligent technologies is crucial:
The first fundamental technology that drives DX in manufacturing is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which is the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial applications. Fueled by big data, AI, automation, and cloud computing, the IIoT enables the connection of industrial machines, devices, and smart sensors to form a responsive ecosystem in which all the equipment communicates and exchanges data in real time. The use of this intelligent technology in production processes brings manufacturers multiple benefits since it allows them to monitor process and equipment performance, identify malfunctions early, minimize downtime, increase operational efficiency and productivity, predict maintenance needs, and refine product quality.
Cloud computing is another fundamental aspect of digital transformation in manufacturing, offering a range of services such as data storage, software, servers, networking, and analytics to foster innovation and efficiency. Manufacturing enterprises leverage cloud-based solutions to access computing resources on-demand at affordable prices, which reduces investment in costly hardware and infrastructure. Cloud computing facilitates real-time data sharing and secure storage in support of various manufacturing processes including inventory tracking, product life cycle management, and ensuring successful enterprise resource planning (ERP).
Powered by AI, the robotics technology is integral for the creation and operation of physical robots. These industrial machines allow for the automation of delicate, physically demanding, or repetitive assembly line tasks with minimal human interference, which significantly enhances productivity and safety at the workplace, as well as reducing labor costs. Cloud robotics, an emerging branch of robotics, is now gaining popularity in digital manufacturing to build and operate physical robots that are connected to the cloud. This allows robots to use computing resources and access real-time data to perform complex tasks while being controlled remotely. In terms of manufacturing, cloud-enabled robots are used in a wide range of applications, including predictive maintenance, quality control, assembly, and packaging. Mordor Intelligence predicts that by 2028, the cloud robotics market will be growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.8%, indicating that increasing numbers of businesses will turn to this innovative technology in the near future.
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector by enabling the creation of three-dimensional objects from digital models. Additive manufacturing significantly contributes to production processes since it allows companies to create rapid prototyping of industrial products and enables on-demand production of customized parts. Furthermore, the adoption of 3D printing in manufacturing enhances design flexibility, allowing for the creation of intricate and sophisticated parts while minimizing waste and promoting environmental sustainability.
Implementing digital twins is a prominent trend in manufacturing digital transformation. In simple terms, a digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical product, process, or system that simulates its behavior and performance in real time. Digital twin technology enables the following:
Augmented reality (AR) is technology that focuses on enhancing the physical world with computer-generated information by overlaying digital content onto real objects and settings. In manufacturing, AR has numerous applications, including employee training, quality control, warehouse management, and workflow optimization. Manufacturers can also implement AR to refine product design and features and provide remote customer support.

According to Gartner, 91% of enterprises across various sectors are involved in digital initiatives, and manufacturing is no exception. Digital manufacturing solutions bring numerous benefits to manufacturers, some of which outlined below:
With the adoption of advanced digital solutions, manufacturers can automate a wide range of manual operations, which drastically increases employee productivity and overall efficiency. In this context, improved efficiency translates into cost reduction and revenue generation.
Automation and digital technologies such as AI, robotics, and ML when integrated into manufacturing processes can significantly refine product quality by minimizing human errors, preventing product defects, and streamlining product development. As a result, higher-quality products are manufactured and offered to buyers, fostering positive customer experience and satisfaction.
By integrating smart technologies into production lines, manufacturers derive immeasurable insights into how to optimize human resources and processes, which enables them to considerably reduce production costs. Moreover, the use of intelligent technologies enables companies to address manufacturing issues at an early stage of product development, resulting in reduced downtime and waste, as well as cost savings.
Providing impeccable customer experience is a top priority for any digital manufacturing company. Looking to align their products with the demands of customers, companies are now adopting a customer-centric approach in which customization and personalization strategies are key elements. The integration of digital solutions into manufacturing processes enables manufacturers to customize products and personalize the shopping experience, thereby improving their image and reputation.
DX is a backbone of digital culture enhancement in a manufacturing organization. Shaped and influenced by digital technologies and tools, a robust digital culture means that employees are willing to embrace the latest innovations and tech solutions to refine production processes, streamline operations, and boost productivity. Consequently, an enhanced digital culture will allow manufacturers to grow, innovate, and stay agile in today’s fast-paced and constantly changing digital landscape.

Although DX provides proven benefits to the manufacturing sector, many manufacturers are hesitant to undergo such radical changes due to the potential challenges. Нere are five barriers that manufacturers should be aware of before embarking on a DX journey.
Digital manufacturing requires substantial financial investment in new technologies, as well as providing the necessary training and upskilling for employees, acquiring new hardware, and upgrading the existing infrastructure. Therefore, a comprehensive DX investment plan should be devised that estimates overall expenditure, calculates the expected return on investment (ROI), and investigates potential cost reduction routes.
Since DX in manufacturing implies a full-scale transformation over time, this can cause stress and resistance among workers. To overcome this hurdle, it is vital for companies to be consistent and transparent, keeping employees informed and engaged in the digital transformation initiatives throughout the entire process. It is also important to gradually transition to DX, which can help employees develop the right mindset to further embrace the emerging digital solutions.
To successfully undergo DX, manufacturing enterprises need to have a skilled workforce that knows how to leverage the new technologies. Nevertheless, there are often technological skills gaps within companies, which slows down DX and holds back progress. The solution to this issue typically involves upskilling the existing personnel and/or employing new talent who are already equipped with the knowledge of the latest DX technologies and tools, and how to effectively use them.
Another challenge that prevents manufacturers from embracing digital solutions is the legacy infrastructure and outdated systems that are likely to be incompatible with the emerging DX technologies. Thus, it is crucial to assess in advance whether certain systems will have to be retired, as well as how much value will be brought to the company upon upgrading to the new ones. Manufacturers can prioritize the areas of their business that must be digitally transformed first to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and generate more revenue.
Digital manufacturing transformation involves the integration of modern technologies into the production processes to create an interconnected ecosystem of smart machines and devices. However, this ecosystem is prone to risks and vulnerabilities that can lead to data breaches, intellectual property theft, and cyberattacks, resulting in manufacturers being even more hesitant about going digital. It is therefore essential to develop a robust security plan that addresses security issues such as the ways to improve security protocols, understand the data flow in an organization, identify and mitigate risks in the event that data is compromised, and protect critical information assets.

In spite of the obstacles that manufacturers face while undergoing DX, there are successful examples of how various manufacturing companies have taken advantage of digital manufacturing services.
The Volvo Group is a multinational manufacturing corporation that produces buses, trucks, construction equipment, and industrial engines. Volvo implemented the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and augmented reality (AR) solutions to meet customer demands for customizable products. These technologies enable the quick identification of defective products, reduce waste, increase customization, and improve customer satisfaction while cutting costs.
Microsoft, an industry leader in producing flagship intelligent devices and developing server-side, productivity, and business solution applications, transformed its IT and business operations in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. By adopting cloud-based architecture, enhanced security, and AI, the company has transformed its business and operating models and established a product-based approach, focused primarily on delivering product value to customers. With the deployment of DX solutions, Microsoft has optimized its production processes, improved business agility, empowered employees, and increased levels of customer engagement.
The Lego Group is a toy production company that is globally renowned for manufacturing interlocking plastic bricks. Having initially set foot in the digital space in the late 1990s, the company had commenced DX, but encountered several business and operational issues, which called for a dramatic change of their production and business operations. DX initiatives have enabled the Lego Group to improve data sharing across the enterprise and leverage 3D printing technology. In addition, the company uses smart technologies to boost its customer engagement by crowdsourcing product design and launching new products, bridging the gap between physical and digital Lego.
Widely known for manufacturing electric cars, Tesla has relied on DX solutions for the creation of the connected cars, which has revolutionized the automotive industry. Connected to the Internet and equipped with radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors, a connected vehicle is capable of collecting and sharing data in real time and making informed decisions, based on this data. This delivers more value to customers as it aids in traffic prediction, predictive maintenance, and emergency assistance on the road. Furthermore, through smart digital manufacturing software, the company offers buyers high levels of vehicle customization by enabling them to choose the wheel designs, color, interior, and autopilot configuration of their new car based on their needs and preferences.
DX has significantly impacted the manufacturing sector. Besides the integration of numerous intelligent technologies into production processes, digital transformation in manufacturing involves a complete rethinking of existing business models and strategies, as well as rebuilding organizational cultures. Although this dramatic change poses several major challenges, there is a pool of significant benefits that DX offers to companies worldwide. Industry leaders, such as Volvo, Microsoft, Lego, and Tesla, have successfully undergone DX, so maybe it is high time you harnessed it, too? Just get in touch with our field experts today to discuss implementing digital solutions in all aspects of your manufacturing business!
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form to receive a consultation and explore how we can assist you and your business.
What happens next?