
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

In this article, we will assess the state of generative AI in the healthcare market, examine use cases of this technology for healthcare organizations, outline its benefits and challenges, and identify best practices for implementation.
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry, providing new opportunities for medical institutions, practitioners, and patients. Despite the current low adoption rates, generative AI in the healthcare sector is expected to reach almost USD 22 billion by 2032, up from just USD 1.45 billion in 2023.
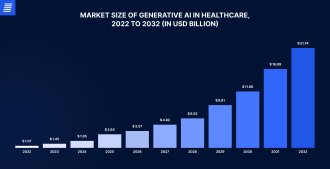

Source: precedenceresearch.com
Approximately 75% of healthcare executives view generative AI as a critical technology capable of transforming the industry. Still, only 6% have a clear strategy for implementing generative AI. The biggest barriers to integration for generative AI are insufficient resources and expertise, as well as compliance risks.
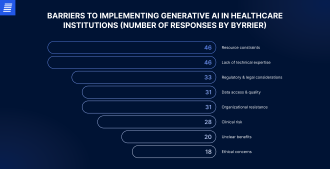

Source: bain.com
Generative AI is reshaping approaches to a wide range of healthcare tasks and challenges, from medical training to personalized patient care. Let’s explore some common generative AI use cases across various healthcare areas.
Practical training using generative AI solutions helps medical students and practitioners develop and perfect essential skills, offering them realistic experiences comparable to real-world scenarios.
Using generative AI along with augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR), medical educational institutions and healthcare providers can mimic real-life scenarios and environments in a safe and controlled setting. Simulation-based learning allows students to apply theoretical concepts in practice, using a trial-and-error process to acquire knowledge and hands-on skills and gain confidence in those skills. Through simulations, medical students and practitioners can examine difficult or unusual cases and prepare for operations. Generative AI is also useful in providing instant feedback and assessing learners’ performance, helping them identify difficult areas requiring more attention.
Generative AI can create personalized educational content for patients, taking into account their conditions, treatment history, and other relevant data. The technology can generate useful information at different reading levels to accommodate various degrees of knowledge, education, and comprehension, improving accessibility for all users.
Medical data analysis and generation play crucial roles in medical decision-making and research aimed at understanding human diseases and identifying new diagnostic methods, prevention strategies, and treatments to improve overall human well-being. Generative AI is emerging as a valuable tool in these areas. Here are several examples of how it aids in medical data analysis and generation.
Generative AI enables natural language processing (NLP) models to comprehend and interpret the context of processed text. This capability facilitates the automated extraction and analysis of data from medical literature, documents, and patient records. For instance, it can be integrated into systems that automatically summarize medical documents and records, uncovering valuable insights for further research and streamlining the decision-making process.
The privacy and security of sensitive health data is one of the main concerns in medical research. Synthetic clinical data resembles actual patient information and can be used in research without compromising privacy. Generative AI, particularly generative adversarial networks (GANs), can be trained to create realistic synthetic medical data incorporating demographics, medical conditions, treatment histories, individual characteristics, and various medical scenarios, thereby improving and accelerating clinical trials and research.
Generative AI can facilitate personalized treatment approaches. The technology can provide tailored solutions for medical treatment and provide answers to patient questions.
Generative AI models can be trained on patient data, electronic health records (EHRs), medical images, clinical measurements, and expert annotations to detect patterns, anomalies, and signs of disease. They can process, understand, and summarize information, creating a holistic overview of a patient’s condition. For healthcare practitioners, this translates to faster and more accurate diagnoses and improved decision-making.
Generative AI can help create targeted treatment plans for unique healthcare cases. By analyzing patient data, individual genetic and clinical profiles, historical data, and other medical records, generative AI models help medical professionals develop personalized medicine plans, improving patient outcomes.
Powered by generative AI, virtual assistants provide patients with personalized support through conversational interactions. They understand and respond to questions, providing answers based on EHRs, patient data, medical guides and protocols, knowledge bases, and information from previous patient interactions.
The healthcare industry involves numerous repetitive administrative tasks that can be automated using generative AI.
Chatbots powered by generative AI can provide responses to patient queries, streamlining administrative operations and allowing medical staff to focus on other tasks.
Generative AI can analyze a medical staff’s current workloads and suggest schedule optimizations, leading to more efficient workflows. It can also automate the process of booking and rescheduling patient appointments, optimizing time management for healthcare practitioners.
Medical personnel can use generative AI to transcribe patient sessions and fill in EHRs and other clinical documentation, freeing time for other tasks. The technology can then provide summaries and actionable insights based on these records.
Generative AI models can create comprehensive structured health reports on medical services, specific conditions, patients, clinical findings, test results, and more. The technology can also be used to generate financial, legal, and compliance reports.
To function effectively, healthcare facilities depend on numerous nonmedical processes and departments, including recruitment, procurement, IT, and finance. Generative AI can assist these teams by creating offer letters, customizing onboarding, drafting contracts, creating purchase orders, developing code, running cybersecurity tests, and more.
The potential impact of generative AI in healthcare is immense. It is expected to completely transform the industry, helping medical personnel perform their jobs more effectively and streamlining processes. Following are some of the key benefits of generative AI that healthcare companies can leverage.
Generative AI can be used to automate repetitive and routine tasks, streamlining processes and making workflows more efficient. This saves time for healthcare personnel, allowing them to focus on tasks that require more attention.
Traditional medical research and treatment is limited by the amount of information humans can perceive. Generative AI is capable of analyzing and learning from vast amounts of historical and current data to produce actionable insights for researchers and practitioners, leading to better outcomes.
Generative AI models are trained on data from various sources and examine various factors that impact decision-making. Thus, these models can identify patterns that may be hidden or initially undetected, improving treatment outcomes.
Solutions powered by generative AI reduce human error through comprehensive analysis and assistance with diagnoses, treatment plans, and outcome predictions. These solutions are also capable of tackling repetitive tasks that burden medical professionals, reducing burnout.
Patients can get quick answers to their questions and promptly deal with administrative issues via virtual assistants and chatbots, receive notifications about required medications and procedures, and schedule and reschedule appointments. Generative AI solutions enable more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans, which increases patient satisfaction and loyalty.
Despite all the advantages of implementing generative AI in healthcare, this technology does come with some risks.
Before implementing a generative AI model, it is essential to evaluate its clinical utility. This assessment is crucial for the deployment of an AI solution and involves determining if the problem being addressed is worth solving, as well as which model to use. In pursuit of accuracy, healthcare companies might choose a model with no clinical utility. However, a more useful model could be less accurate. In such cases, decision curve analysis can identify the most applicable and beneficial generative AI model for the specific healthcare application.
Generative AI models are trained on large amounts of data, including personal health information and other sensitive data, which puts this information at risk. To avoid data breaches and ensure the safety of patient information, healthcare institutions must comply with data protection regulations and follow industry standards, such as HIPAA, and local policies, such as the GDPR in the EU.
Implementing generative AI solutions is a key component of the digital transformation process that many healthcare organizations are pursuing. However, numerous companies still have legacy systems that are incompatible with advanced technologies. Before integrating generative AI into their processes, healthcare organizations must assess the current state of their IT infrastructure and ensure it can accommodate new AI tools. It is also essential to cleanse and standardize data so AI models will work properly and generate relevant output.
Generative AI model outputs rely heavily on the quality of the training data. If the training data is biased or inaccurately represents the population, the results will also lack diversity and inclusion. To address this challenge, healthcare organizations should incorporate data processing and validation techniques to detect and correct bias and errors, and continuously monitor system outputs.
Despite the accuracy that generative AI can offer, the technology is still evolving and is not immune to errors. There is also the risk of AI hallucinations, where a generative AI model produces nonsensical or misleading outputs due to incorrect assumptions, insufficient data, or biases in the data. To mitigate this risk, human review of AI-generated outputs is essential. Enhancing transparency in the development and deployment of AI solutions, including the data they are trained on and the methods they use to generate outputs, can also help address this issue.
The feasibility of a generative AI model relies on many aspects, including data quality and availability, deployment challenges, and maintenance. It is important to use relevant data, ensure representation, and make data processing transparent. An AI solution must be clinically valid and generate clinically meaningful outputs. However, this can be difficult to evaluate because healthcare companies often rely on their own experience or that of their colleagues.
The best practices for integrating generative AI solutions into healthcare processes are based on the challenges this technology presents.
Changing processes and workflows in the healthcare industry is not easy. Organizations must first assess their requirements and determine how advanced technologies like generative AI can best serve them.
Key questions to consider include:
Another important step is to evaluate all the risks and challenges associated with integrating generative AI into healthcare processes and develop a plan to address them. This includes assessing the IT infrastructure and the readiness of the personnel to adopt this technology. Healthcare organizations should prepare their technological resources and ensure they can effectively leverage generative AI models.
The datasets used to train generative AI models directly impact the results they generate. Accurate, high-quality input data is essential for obtaining valuable outcomes and minimizing the risk of faulty or harmful outputs. To ensure the fidelity, quality, and security of the data, healthcare organizations should consider partnering with technology experts to assist with data preparation.
When integrating generative AI solutions into a healthcare organization’s workflows, a key concern is how personnel will interact with the technology. Providing educational support and establishing guidelines for using these new tools is essential. Generative AI should improve efficiency and facilitate work, not create barriers for employees.
An experienced technology partner is crucial for the successful implementation of a generative AI solution. The potential vendor should comply with healthcare industry standards and local regulations and have domain expertise to deliver a comprehensive and reliable product.
The use cases for generative AI in healthcare demonstrate its importance, transformative impact on the industry, and potential to advance and streamline processes such as diagnosis and patient treatment. Despite the challenges, generative AI solutions are designed to improve healthcare outcomes. To learn more about generative AI and take the first step toward adopting this new technology, contact our team.

Generative AI is a technology that can learn from existing data to produce new, high-quality content. In healthcare, generative AI models trained on medical record data can facilitate various processes, including diagnosis, administrative procedures, patient interaction, and more.
The key difference between the two types of AI is their capabilities and use cases. Traditional AI is used for data analysis and forecasting. Generative AI creates new data based on training data.
The cost of a generative AI solution depends on many factors, including the type of model, the tasks it will perform, the implementation approach, customization options, and more. Contact our team, share your idea, and receive a project estimate tailored to your needs.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659