
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
In this article, we will define healthcare data management, explore the benefits and challenges of implementing data management systems, and share best practices for their development.
Health data management refers to the process of handling healthcare data in digital form. This data includes patients’ personal information and health history, medical notes, prescriptions, health surveys, laboratory tests, imaging results, claims (e.g., payers), and more.
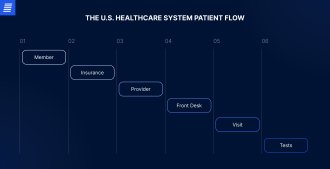
Within healthcare delivery systems, data is used by multiple stakeholders and managed by different systems. Various stakeholders have their own objectives and needs when it comes to data, as well as different levels of access to data. Let’s review what data sources are valuable to stakeholders, taking the U.S. healthcare system as an example.
| Role | Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | These are individuals who receive any kind of healthcare service. To ensure that their treatment is relevant and timely, patients can provide and validate information for providers and intermediaries. | Personal health records (PHRs), health history, immunizations, allergies, and personal information. |
| Providers | These are individuals or entities delivering healthcare services to patients. They include nurses, physicians, therapists, clinics, and hospitals. | Electronic medical records (EMRs), electronic health records (EHRs), hospital data, administrative databases, claims data, patient/disease registries, health surveys, imaging systems, laboratory information systems, medical devices. |
| Intermediaries | These are entities that act as a link between patients and providers. They include organizations that collect and manage funds and use them to cover the healthcare expenses of members (people paying into these funds), including insurance companies and government payers. | Enrollment information, member demographics, claims data, care gaps, financials. |
Health data management solutions address specific needs and issues and can be used for the following key purposes:
Health data management systems help track and measure the performance of healthcare organizations and medical practitioners, including readmission rates and patient satisfaction, thus allowing healthcare providers to take the necessary measures to enhance patient care. Insights acquired through effective data management and analysis can be used to develop effective action plans, providing recommendations for doctors on how to treat patients. Moreover, by identifying high-risk patients who need additional care or intervention, healthcare providers can prevent complications and improve long-term health.
Data management in healthcare allows providers to identify areas of inefficiency or resource waste in care delivery—such as unnecessary tests and procedures, hospital admissions, and no-shows—and revise their resource allocation policies accordingly. Health data management solutions provide insights into the value and efficiency of the care delivery of a certain healthcare provider, which can be used to negotiate cost-efficient reimbursement rates with payers.
In the healthcare industry, decision-making occurs in various spheres of patient care, from diagnosing to strategic management issues. Since it influences people’s lives, healthcare providers must understand the current situation and trends and base their decisions on comprehensive and reliable information using effective data management systems.
By implementing a data management system, medical organizations can track their performance and productivity; support their business strategies, including finance management; and streamline administrative processes, such as claims processing and schedule coordination for healthcare workers.

A comprehensive approach to data management in healthcare involves several essential processes.
To ensure data security, improve its quality, and reduce data silos, different policies, standards, and actions are applied. These policies define how data is managed and govern the way it is gathered, processed, stored, and accessed. A single source of truth is created based on these standards and policies. For example, data governance policies might outline data access levels for different personnel or specify data encryption methods for storage.
Data is gathered from different sources, such as EHRs, EMRs, PHRs, medical devices, apps, and services, and is transformed into a unified, consistent format. For example, data from disparate systems might be standardized to a common data model, like HL7 FHIR.
Data is augmented and verified to increase its utility and value and prepare it for further analysis.
Health data is stored in a secure and accessible repository, such as a data warehouse.
By analyzing health data, medical organizations can uncover valuable insights and patterns for further decision-making.
The following are the key benefits data management systems offer to clinics.
Health data management systems provide healthcare workers with a holistic view of a patient, enabling accurate diagnosing and well-informed clinical decisions. Treatment plans can be adjusted to consider individual patient information, including health history, lab tests, screening, and imaging results.
A comprehensive medical data management solution gives healthcare practitioners access to different types of healthcare information, from membership information to a comprehensive patient’s medical history and prescriptions. This enables healthcare practitioners to reduce errors and find reliable solutions. Based on insights acquired from data management systems, it is possible to track health trends within a certain group of people or a larger population to take proactive measures and identify areas for improvement.
Patient flow, wait times, and optimized administrative processes and procedures rely on the efficiency of data storage and management. A single and reliable source of information facilitates these processes by removing the need for paper-based documentation, providing access to full patient data, reducing risks of administrative mistakes, and automating tasks, including data entry.
An efficient healthcare data management system serves as a single source of truth for analysts, researchers, and clinical scientists, providing actionable insights and uncovering patterns. This can help in further analysis and research, improving diagnostics and predictions, and supporting preventive patient care.
The process of building a compelling healthcare data management system poses some challenges that require attention.
Different data sources and data storage formats, as well as manual data entry, cause inconsistent formats; duplicated, inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate data records; data silos; and security concerns. When managing diverse data sources, it’s important to establish rules for connection and uploading data and create unified data formats for raw-level storage. By standardizing, cleaning, and linking data, healthcare organizations can create a single source of truth for health data, eliminating administrative and medical errors and enabling reliable and accurate analytics. Data linking also enables cross-source reporting, for example, gathering and reporting on a patient’s data from different sources.

A centralized data warehouse and Microsoft Power BI allow collecting and analyzing data from the divisions scattered across the USA.
The amount of data the healthcare industry generates is increasing at a rapid pace. It is also significantly underused. According to various sources, only 3% to 5% of medical data is utilized properly and provides value. Healthcare organizations that aim to use the available information to its full potential should ensure that incoming data is automatically classified, linked, and converted into a usable format. To get valuable insights from the available data, it should be properly processed and visualized. System scalability is also an important aspect of dealing with expanding datasets.
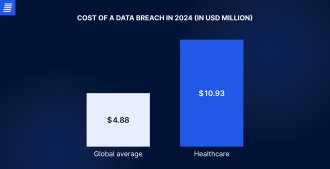
Data breaches and hacking incidents lead to significant resource losses. In 2024, the average cost of a data breach has reached an all-time high of USD 4.88 million, while in the healthcare sector, the average has reached USD 10.93 million. Regulatory requirements and standards ensure that sensitive patient information and medical data are secure. To ensure compliance, healthcare providers must adhere to global regulations and local industry legislation, such as GDPR and HIPAA.

When creating a high-quality solution for health data management, having a reliable and experienced software development partner is crucial. EffectiveSoft assists medical organizations in building smart and effective systems. Here are several examples of data management solutions we developed for companies in healthcare.
For one of our clients, a leading U.S. provider of managed healthcare services with a growing network of healthcare facilities, we developed a reliable data warehouse along with an analytical and reporting tool. The solution designed and implemented by our engineers deals with the increasing number of diverse data sources and systems generating data, ensuring data consistency by transforming it into a single format. Using Microsoft Azure services, we resolved a major issue related to distributed data collection, cleansing, and normalization. Integrating Power BI into the data warehouse offered advanced business intelligence and analytics capabilities.
To solve our client’s challenge of managing large volumes of patient data, EffectiveSoft engineers developed a comprehensive patient data platform seamlessly integrated with the existing EHR system. Leveraging AI and natural language processing (NLP), we merged legacy data, integrated medical imaging, and implemented an NLP-powered semantic search engine and single patient profile. The solution helped improve patient care and operational efficiency and enabled more accurate diagnoses by providing healthcare practitioners with fast access to accurate, comprehensive, reliable patient information.
Health data significantly impacts every aspect of healthcare service delivery, highlighting the importance of a powerful health data management system. To design a comprehensive solution, healthcare organizations must understand the challenges of this process and how to address them, while also finding a reliable partner to implement the system. Contact our team to learn more about data management solutions in healthcare and launch your project.

Effective strategies to improve physician alignment include providing training and coaching on data and documentation, measuring performance based on data from different sources, and providing physicians with valuable information using efficient tools, such as data visualization tools. These strategies provide actionable insights that can support management decisions and engage physicians in care redesign.
EffectiveSoft is an outsourcing software development company with over 20 years of experience in the IT field. Our commitment to delivering cutting-edge solutions to healthcare companies earned us the title of Top Consulting Company in the medical industry by Clutch. Health data and document management systems created by EffectiveSoft engineers enable our clients to improve clinical and management decision-making, enhance collaboration between different medical specialists and facilities, and secure health data.
The cost of a health data management solution depends on multiple factors, including development and customization costs, licensing fees, and the maintenance and support of the system. Integrating advanced technologies also adds to the final cost. Contact our team to get a project estimate based on your needs and requirements.
The main role of data privacy and security in health data management is to protect personal patient information and other sensitive data against cyberattacks and ensure system integrity. Data security in healthcare is governed by different regulations and standards on both local and global levels, such as GDPR and HIPAA.
With the advancement of technologies, health data management is also changing. Medical organizations are increasingly adopting the Internet of Medical Things for collecting data and artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms for managing and analyzing data. A shift from reactive to proactive care entails increased use of predictive analytics to identify high-risk patients early and develop an effective personalized care plan.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659