Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

A decade ago, AI-powered diagnostics or 3D-printed prosthetics seemed like science fiction.

Today, they are becoming a new medical reality. New technologies have enabled healthcare that is proactive, cost-effective, while still patient-oriented. Within the next ten years, healthcare will be unrecognizable.
This article explores the technologies in healthcare that are changing the face of medicine, and how they’re being used to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs while maintaining safety.
Healthcare is no longer limited to reacting solely to active symptoms. New technologies have given healthcare professionals the ability to proactively detect risk factors and identify conditions in their earliest, still treatable stages. Genome sequencing technologies, mobile health apps, nanosensors and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming the way healthcare professionals detect and diagnose diseases.
Whole-genome sequencing has enabled scientists to map the entire genetic code of individuals. This breakthrough has unlocked unparalleled opportunities to understand correlations between specific genes and the development of certain types of cancer and other diseases. By combining these insights with healthcare information, such as data collected from wearables, AI algorithms can identify patterns that indicate predispositions before visible symptoms occur. Ingestible nanobiosensors so small that they are barely detectable with the human eye, are being developed to continuously monitor internal systems on a long-term basis without unnecessary invasive procedures.
Gene therapies are also being explored to investigate the genetic roots of diseases. One such example is CRISPR-Cas9 technology, which enables the editing of specific sections within a gene’s DNA sequence, while deactivating genes that cause diseases or correcting harmful mutations.
This technique harnesses natural immune defense mechanisms to repair DNA by adding or removing specific segments. Scientists are exploring gene therapies to treat genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and Duchene muscular dystrophy, as well as certain types of cancer.
Another exciting invention poised to transform cancer diagnostics is “liquid biopsies”. This non-invasive method utilizes blood tests instead of needles to detect tumor cells or their DNA fragments in the bloodstream long before the signs of disease manifest. Liquid biopsies are particularly valuable for diagnosing lung, colon or prostate cancer. Coupled with advances in gene therapies that can identify and correct DNA errors associated with diseases, this method is opening the door to an era in which conditions can be treated at their root causes rather than merely temporarily managed.
These diagnostic breakthroughs are fueling the emergence and evolution of personalized medicine. By gaining insights into an individual’s unique genetic profile and risk factors, doctors can design customized screening and testing schedules and precise treatment regimens, all tailored to the specific needs of each patient, rather than applying standardized guidelines and protocols.
AI, particularly machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), are invaluable for further personalizing healthcare because of their ability to process vast amounts of information, uncover unusual patterns within large datasets, and implement predictive modeling for evidence-based diagnostics. AI is helping researchers analyze numerous genomic and health records to identify smaller patient subgroups that can benefit the most from targeted screening efforts. Additionally, treatment strategies are becoming increasingly tailored to the individual’s molecular profile and expected response.
Technological advancements in diagnostics and personalized medicine enable a shift from reactive to proactive disease detection and diagnosis, ensuring that the right treatment is delivered to the right patient at the right time.

In addition to advanced diagnostics, new technology is also changing the way medicine is practiced. Automation, advanced treatments, and remote monitoring are paving the way for next-generation procedures. Combined with cutting-edge robotics, AI, 3D bioprinting and digital health tools, they are enhancing healthcare delivery in groundbreaking ways.
In operating rooms, robotic systems, such as da Vinci and Maevas GRAVITY, have revolutionized surgical procedures, offering more precise and less invasive surgeries with increased safety and control. Such systems feature robotic arms controlled by surgeons, a console where the surgeon sits during procedures, and telemanipulation technology that allows direct control and provides visual feedback during the procedure. In addition to enabling extreme precision, this method gives surgeons a way to access hard-to-reach areas in the body.
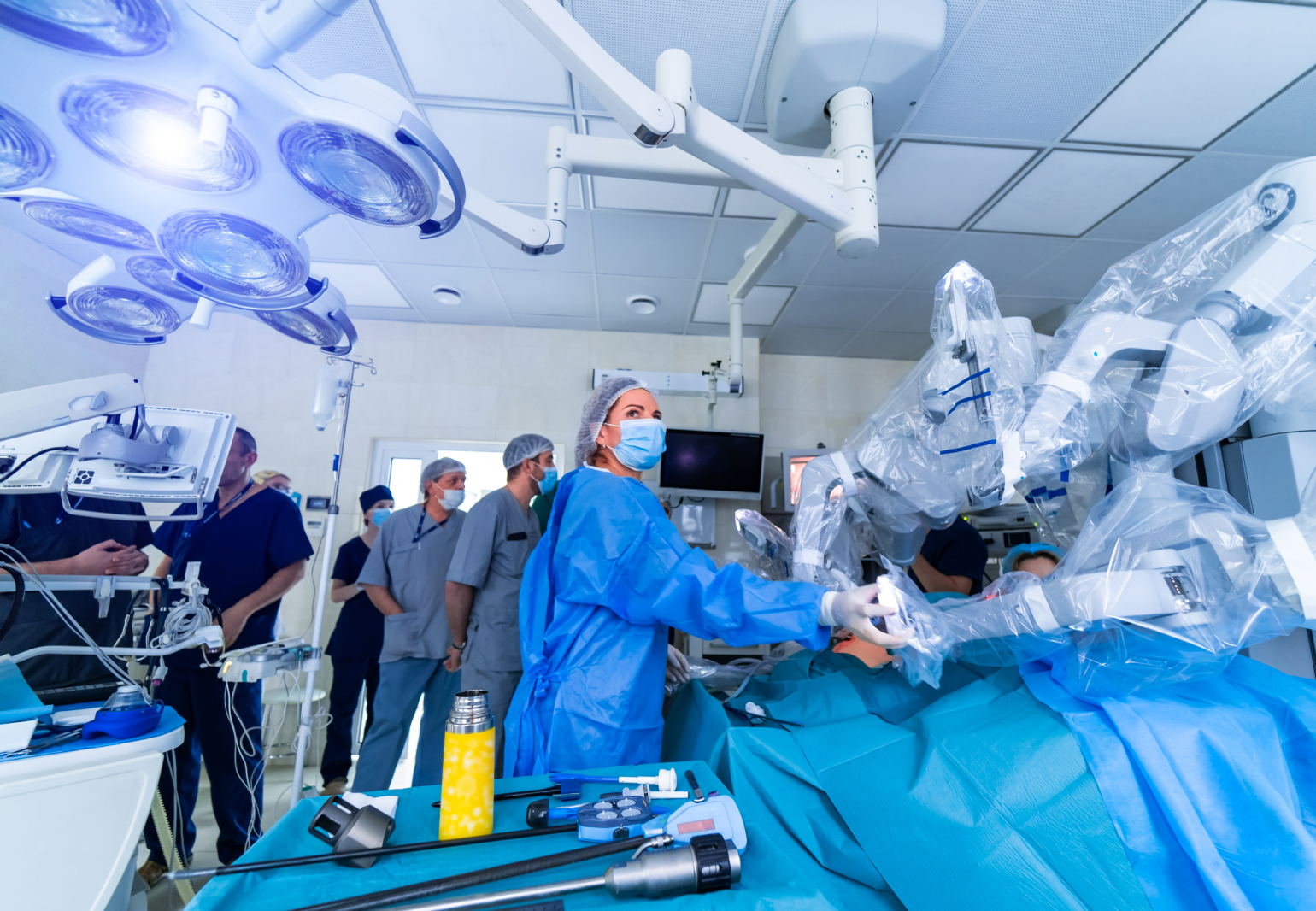
Another healthcare-changing technology that supports robotic-based surgical procedures is image-guided surgery, which provides real-time imaging during procedures. This technology combines preoperative imaging data (such as CT scans or MRI scans) with intraoperative imaging devices, allowing surgeons to visualize the patient’s anatomy in real time. By overlaying these images onto the surgical field, surgeons can accurately navigate through complex anatomical structures and target specific areas for intervention with enhanced precision and lower risk of complications.
Computer-assisted surgery also involves the use of simulation and planning software. These tools allow surgeons to practice complex procedures, test different approaches, and evaluate potential outcomes in a virtual environment before performing them on actual patients. This preoperative planning helps optimize surgical techniques, reduce operative time, and minimize the risk of complications. Patients undergoing procedures such as cardiac bypass, prostate surgery, and hysterectomy, and certain joint replacements can now benefit from these techniques, which involve less pain, blood loss, and tissue damage, as well as shorter recovery times.
Surgical simulation can also be used for training purposes, allowing surgeons to enhance their skills in a safe and controlled environment.
To enable precise visual guidance during critical surgical procedures, augmented reality (AR) technology is being implemented in surgical fields. AR provides vital patient information without visually obstructing the surgical site or causing any distractions, which is an impressive step forward in advancing surgical techniques.
Outside the operating room, scientists are making strides to engineer customized transplantable organs for patients.
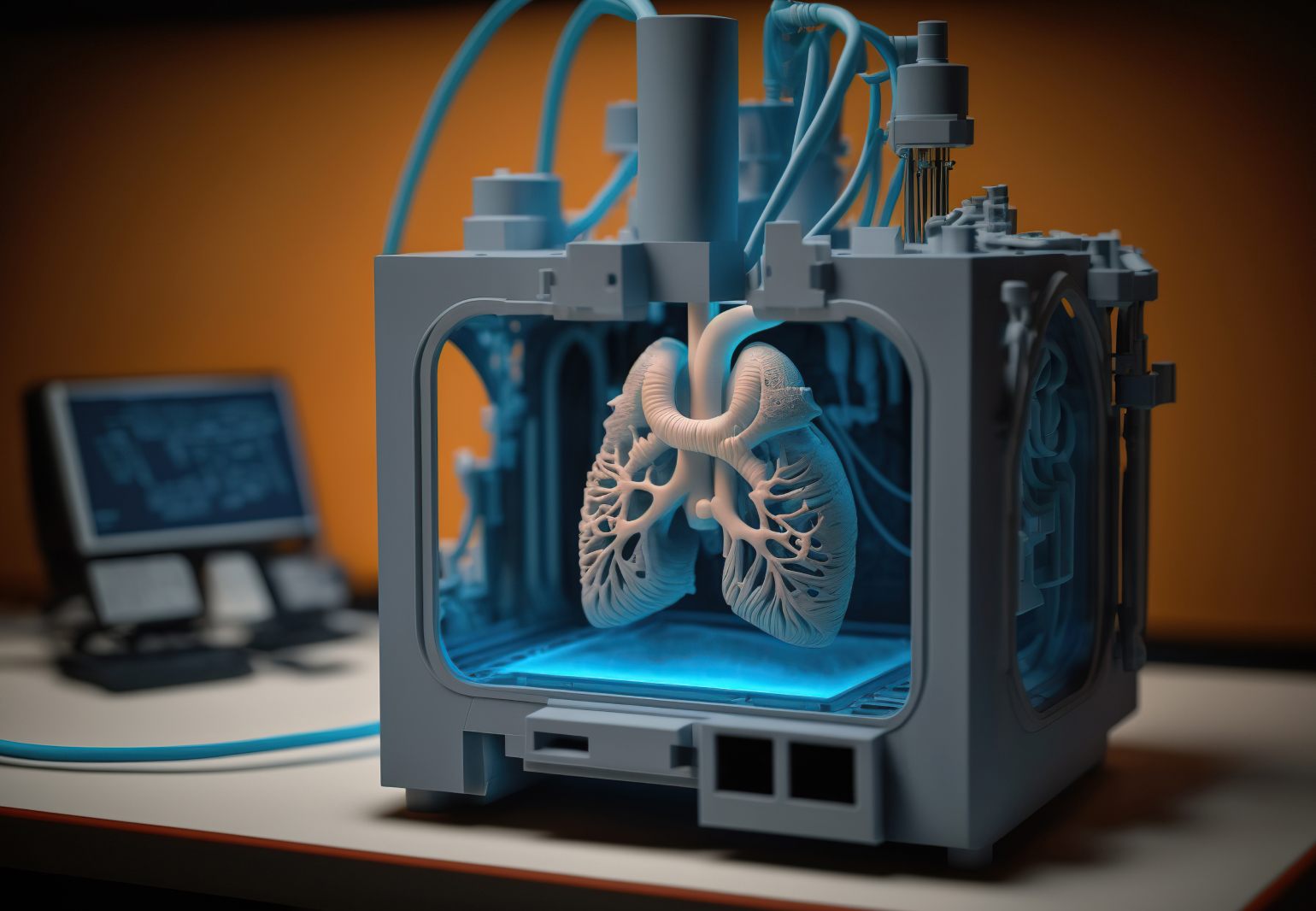

Scientists have already succeeded in creating miniature functioning structures of vital organs like the liver and kidney, as well as vascular networks, by meticulously layering live cells, biomaterials, and growth factors. This progress has been facilitated by advancements in imaging technologies like CT and MRI scans, which provide highly detailed and complex structures that can be replicated with unparalleled precision. While the current focus is on biocompatibility and vascularization, the ultimate objective is to print transplantable, full-size organs equipped with vascular networks to address the global organ shortage and reduce the risk of organ rejection.
Furthermore, future-gen healthcare technologies are improving chronic disease management and access to care today. Chronic diseases are long-term medical conditions that require ongoing management and care. New remote monitoring technologies provide unprecedented opportunities for chronic disease management at home, involving the use of wearable devices and sensors to collect patient data outside of traditional healthcare settings. These intelligent systems, which are often integrated with AI-powered assistants, allow healthcare practitioners to monitor vital signs, medication adherence, symptoms, activity levels, blood glucose levels, and other relevant health metrics. These developments along with telemedicine apps and digital health records ensure that healthcare accessibility extends beyond hospitals to patients’ comfort zones, reshaping the landscape of chronic disease management.
Future technologies in the healthcare field pose promising solutions to the increasing pressure on healthcare systems worldwide, such as rising costs, an aging population, and a growing crisis of chronic diseases. In response, healthcare industry professionals are turning to new technologies to improve patient outcomes while reducing costs.
One of the most significant challenges healthcare providers face is mounting administrative burdens. Paperwork, data entry, and other administrative tasks are time- and resource-intensive. This is where AI assistants and bots can prove immensely beneficial.
AI assistants and chatbots undertake basic assignments such as managing documentation and referrals, securing prior authorizations, scheduling appointments, answering patient queries, updating medical records, and more. By automating these tasks, AI significantly increases the efficiency of everyday healthcare operations and simultaneously reduces excessive costs.
The potential applications of AI in healthcare extend beyond chatbots and assistants, with even more potential to reduce costs. Following are a few additional areas where AI is paving transformational paths.
Atomwise aims to reduce drug development costs by employing supercomputers to predict from a library of molecular structures, which potential treatments will be successful and which won’t. Atomwise’s deep convolutional neural network, AtomNet, daily inspects more than 100 million compounds.
Google’s Med-PaLM language model was specifically created for medical tasks and can understand medical terminology and jargon and generate texts relevant to medical diagnoses, treatments, and patient care. Some of its potential applications are clinical decision support with real-time, evidence-based recommendations for diagnosis, treatment, and patient care as well as medical research in which it can be used to analyze large amounts of medical data and identify patterns, trends, and insights to inform medical research and development.
Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology also has compelling potential applications for healthcare. By enabling the secure sharing of healthcare data between insurers, providers and suppliers on an encrypted network, it can facilitate more coordinated, value-based care. Outcomes-focused agreements between all stakeholders can shift the delivery of healthcare services toward quality over quantity. Streamlining billing through blockchain smart contracts could further reduce expenses.
In addition, virtual and augmented reality offer lower-cost alternatives to conventional learning methods. Medical education traditionally involves expensive cadaver-based training or simulation centers. VR provides a cost-effective alternative by offering realistic virtual environments where medical students and professionals can practice various procedures without the need for physical resources. This reduces the costs associated with traditional training methods while ensuring a safe and controlled learning environment.
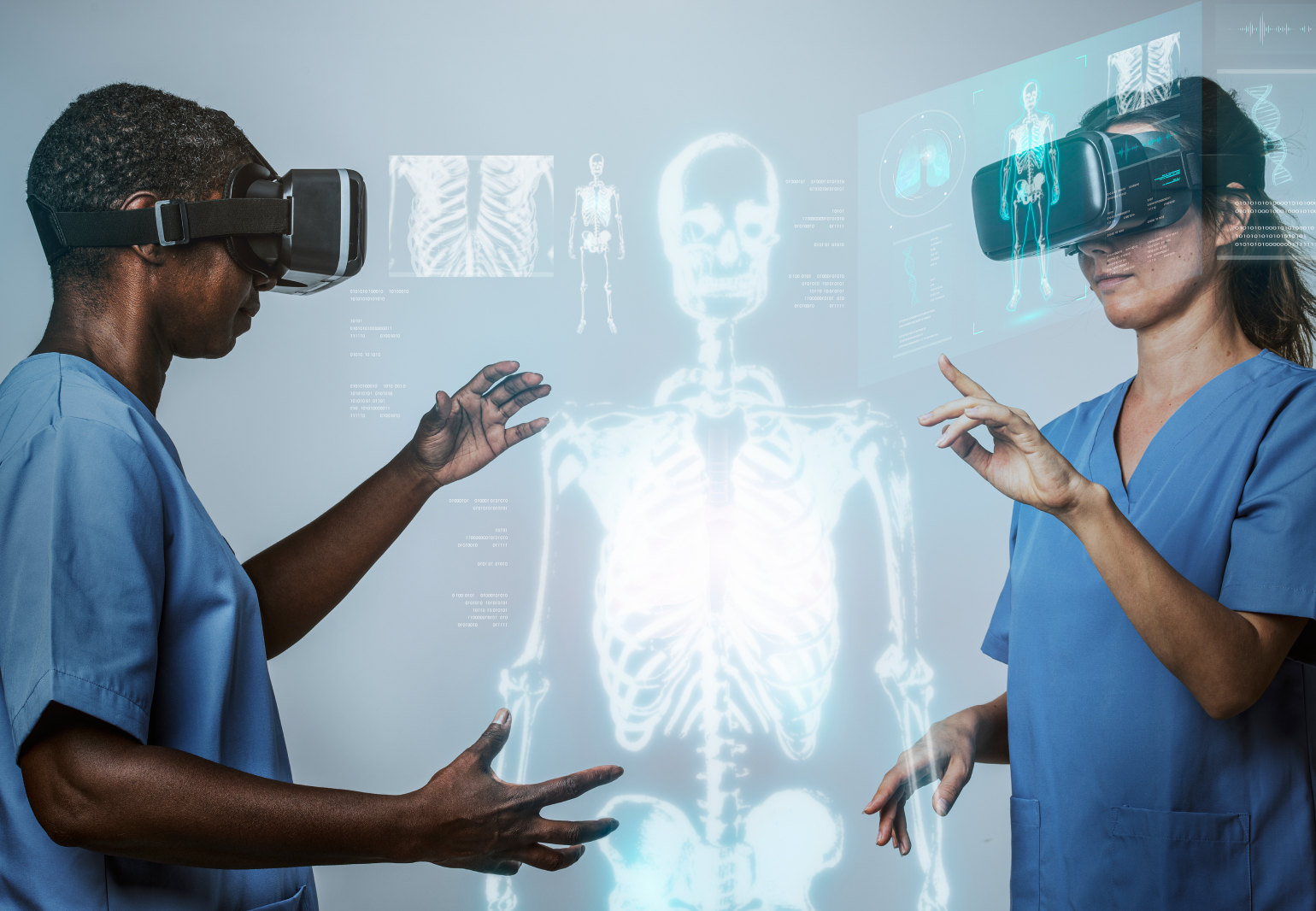

VR can also help reduce healthcare costs by improving patient outcomes. Often combined with AR technology, VR is being applied as a non-pharmacological method of pain management, reducing the need for costly medications and invasive procedures. Studies have shown that immersive VR experiences can distract patients from pain and anxiety during medical procedures, leading to reduced pain perception and decreased reliance on pain medication. Additionally, VR can be utilized in rehabilitation programs to enhance motor skills and cognitive functions, resulting in faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
AI models, blockchain technology, VR and AR offer promising solutions to transform the healthcare industry, making it more efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centered.
The rapid advancement of innovative technologies is changing the healthcare industry at an unprecedented pace. What was once considered science fiction is quickly becoming a new reality. These emerging technologies offer great promise to improve health outcomes, increase access to care, and reduce costs over the long term. Of course, such progress also introduces new challenges surrounding the privacy and security of personal health data. However, if guided wisely with oversight focused on patient well-being and scientific standards, emerging technologies can help change healthcare delivery for the better. Our company welcomes new technologies and those who invest in them for a healthier future. Contact us if you have a need for healthcare software development.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form to receive a consultation and explore how we can assist you and your business.
What happens next?