Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
There is no doubt that healthcare is increasingly going online. From tracking vitals to automating practice management, healthcare apps have revolutionized the experience for both patients and medical care givers by putting care in the palms of their hands.
According to recent industry reports and market analysis, the healthcare mobile app market is expected to continue its rapid expansion in the coming years. The global market size is projected to reach new heights, driven by factors such as the increasing adoption of digital health solutions, rising healthcare costs, and the need for remote patient monitoring.
In this article, we will explore how you can harness the power of programming to develop a customized healthcare app. We will discuss essential features, development considerations, and design fundamentals to ensure your app improves the lives of patients, advances care and makes medical management more convenient than ever.
Today, healthcare application is becoming more than just a buzzword, but an integral part of the healthcare ecosystem. Before we delve into healthcare application development, we must explore the exact definition of a healthcare app in all its dimensions.
In essence, a healthcare application is a software solution designed to improve efficiency and foster better communication between healthcare professionals, patients, or caregivers. These applications can be used on a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops, and offer a broad range of functionalities, including tracking medication adherence, monitoring chronic conditions, scheduling appointments, communicating with healthcare providers, and more.
Further refining the concept, it is worth noting that the terms “healthcare app”, “medical app”, and “wellness app” are often miscategorized and thus used interchangeably. The distinctions are quite nuanced.
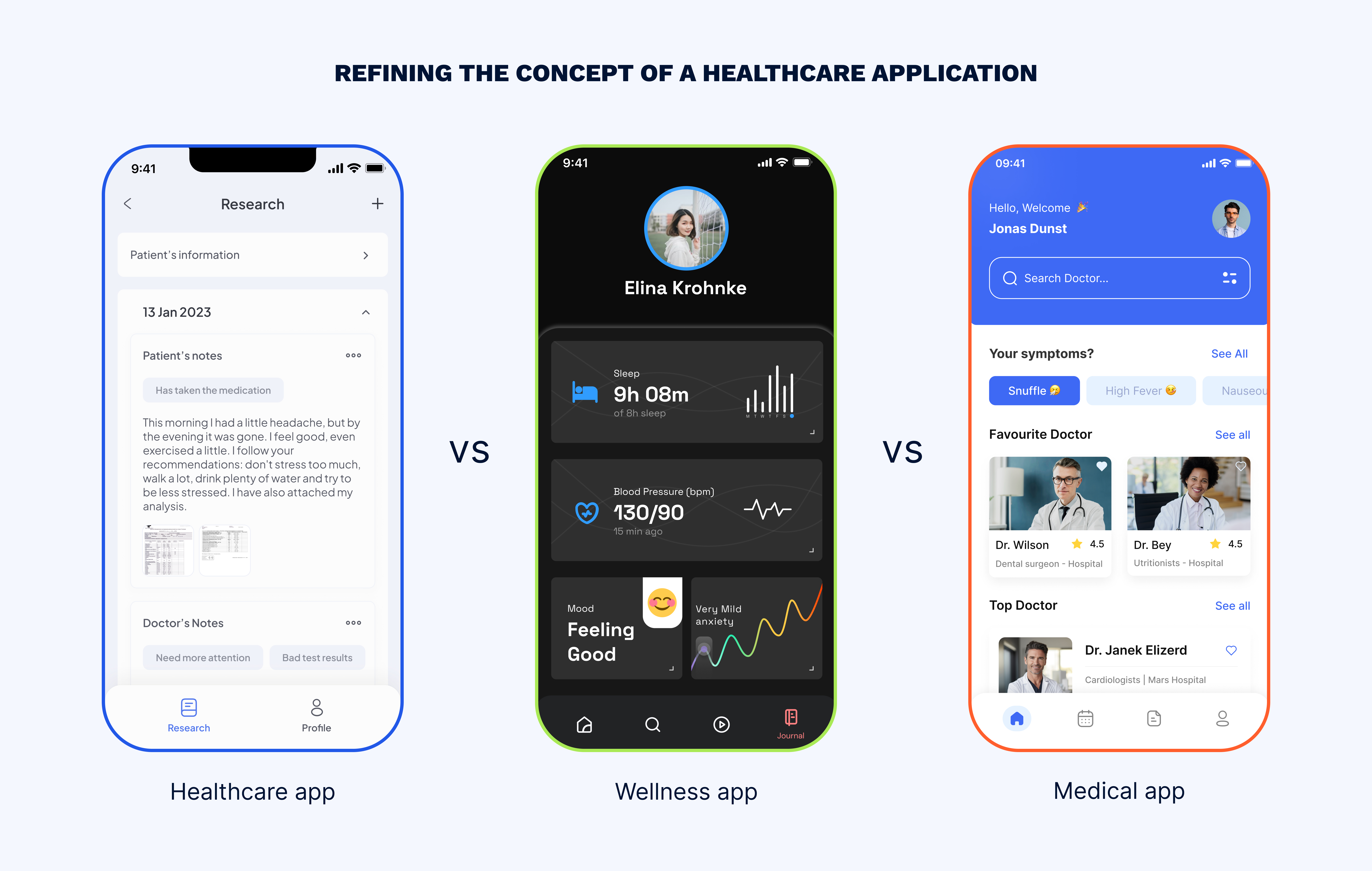
The main differences between the three are their purpose and target audience. Medical applications are mainly designed for healthcare professionals, who use them to diagnose, treat, and manage the health of their patients. These applications typically require a high level of security and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, as they involve sensitive patient data. Common features include electronic health records, radiology and lab results, medication management, and clinical decision support.
Contrastingly, healthcare applications aim to streamline the delivery, accessibility, and management of healthcare services. These applications may be used by various stakeholders within the healthcare ecosystem, including healthcare providers, payers, or patients. Healthcare applications may include features such as practice management, billing and insurance claims, patient scheduling, and health information exchange.
Wellness applications narrow their focus on maintaining and improving health and well-being for individuals. These applications may offer fitness tracking, nutrition and meal planning, and health education.

Now that we’ve provided an overview, let’s delve into the types of healthcare applications available in today’s market.
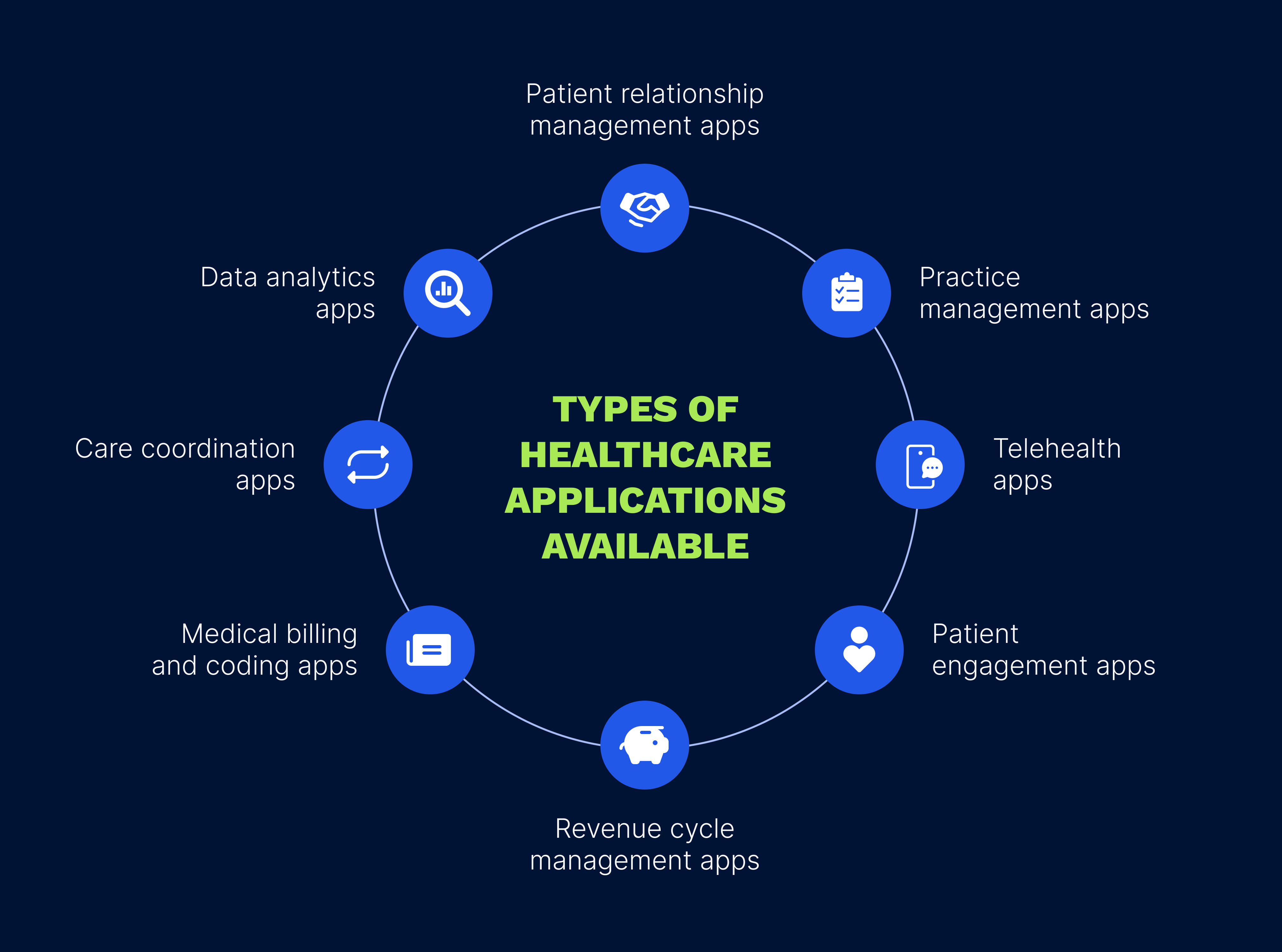
Conveniently facilitating remote patient-doctor interactions, often through video conferencing or messaging, telehealth apps can be used for routine check-ups, follow-up appointments, and remote monitoring. In addition, telehealth apps are crucial in reducing the workload of healthcare facilities and lowering the risk of spreading infectious diseases.
Streamlining the day-to-day operations of small and medium-sized medical practices and clinics, practice management apps encompass appointment scheduling, billing, insurance claim submission and reporting to increase administrative efficiency. These apps can also provide analytics and reporting functionality to improve practice performance.
These apps aid healthcare providers in documenting and processing medical services for insurance reimbursement. This can include generating claims, tracking payments, managing reimbursements, and more, often combined with code lookup and compliance checking tools. In short, medical coding and billing apps target the tasks associated with translating clinical information into billable codes and facilitating the billing process.
These apps empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare by providing education, support, and respective tools. Patient engagement apps facilitate personalized health information, medication reminders, symptom tracking, appointment scheduling, and secure messaging. They support remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and seamless data integration. Patient engagement apps play an essential role in the shift toward patient-centered care.
A true asset for healthcare providers, these applications streamline the financial life cycle of a patient from determining patient eligibility and collecting copays to submitting claims and following up on unpaid accounts. Revenue cycle management apps aim to optimize the financial performance of a healthcare organization by streamlining processes, reducing errors, and accelerating reimbursement.
These apps help healthcare providers analyze data to improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and optimize operations. Data analytics apps can include data visualization tools to help providers easily view and understand complex data sets, as well as predictive analytics to identify trends and forecast future patient needs.
These solutions empower care teams to continuously engage patients by leveraging personalized outreach, real-time surveys and reward programs that promote healthy behaviors, collectively driving higher satisfaction ratings, adherence to treatment plans, and practice retention over the long term.
Building upon the foundation of inter-provider collaboration, these applications simplify referral management, care planning, and communication among different providers. These apps enable seamless transitions between providers, eliminate redundancy in services, identify potential gaps in care, and manage care across different settings and providers.
In order to achieve their primary objective of connecting patients with caregivers, healthcare applications must incorporate the following features:
Today’s healthcare apps place the patient experience first by providing intuitive tools to manage the health needs. Frontend frameworks such as React facilitate the building of responsive web and mobile app portals that adapt to any device size or platform. Server-side rendering for apps with complex content improves mobile performance while intuitive navigation informed by user testing enables patients to easily access features like medical records, appointment scheduling, billing and payments functionality, telehealth modules, and personalized health resources.
Direct HIPAA-compliant communication between patients and care teams is facilitated through secure messaging modules. To guarantee reliable protection of communication data, the modules use end-to-end encryption, with TLS and AES-256 protocols used for data in transit and at rest, respectively. APIs compliant with Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) standards allow for integration with electronic health records (EHR) and clinical messaging platforms. This allows patients and doctors to communicate conveniently via text, audio or video.
The integration of secure payment gateways enables seamless digital billing and coordination with insurers, streamlining the payment process for patients and healthcare providers alike. With electronic invoicing via automated billing workflows, invoices are sent to payers automatically. Real-time payment processing is made possible through webhooks, which capture and process payments instantly as transactions occur. Integration with practice management systems enables secure exchange of the billing and clinical data by employing HL7 and FHIR API standards for bi-directional data sharing. The tokenization of raw payment data outside the server-side ensures PCI compliance and adds an extra layer of security to protect sensitive payment information.
Healthcare applications should enable the direct collection of crucial vital signs like blood pressure, oxygen levels and weight from supported devices. Integration with software development kits (SDKs) such as HealthKit for iOS and Google Fit SDK for Android facilitates this data gathering. The collected data can then be transmitted using secure protocols such as Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT). Next, this data is often sent to cloud-based storage solutions integrated into environments like AWS IoT Core or Greengrass, which serve as data lakes designed to handle large volumes and varieties of health data. Subsequently, artificial intelligence can be employed for data processing, utilizing advanced analytics to identify longitudinal trends and provide valuable insights./p>
HIPAA-compliant video and audio conferencing capabilities powered by services like Twilio Programmable Video and embedded in a React/Next.js responsive site or mobile healthcare app built with React Native or other frameworks, can expand healthcare access in underserved areas or during public health emergencies by supplementing in-person visits. HIPAA compliance ensures that patient privacy and confidentiality are maintained. Adding file sharing enhances the quality of virtual care, streamlines the consultation process, and facilitates informed decision-making.
Together, features such as secure payment gateways, remote monitoring, security components, and more, when combined with user-centered design, empower healthcare applications to be the foundation of convenient and accessible care. These functionalities play a pivotal role in enhancing collaboration among care teams and improving patient outcomes.
Developing software for the healthcare industry demands diligence beyond just code. Following are some of the most crucial considerations for creating impactful healthcare apps.
The initial point in healthcare app development involves defining the target audience, which could include clinicians, administrative staff, or patients. Understanding the specific needs of the people who will use the app guides the development process and facilitates the creation of a valuable healthcare product.
Interoperability, data standards, hosting requirements and technology choices require thorough upfront analysis. Incorporating standards like FHIR and SNOMED-CT helps futureproof APIs. In situations requiring low-latency remote monitoring, edge computing may become essential.
Applicable regulations based on product classification and data handled must be identified. This may include HIPAA, FDA, Common Rule and state laws governing telehealth and prescribing. Incorporating embedded compliance capabilities and adopting a proactive compliance-by-design approach may reduce potential risks and provide corresponding protection.
The sustainability of a product depends on the chosen monetization strategy, whether through subscriptions, claims processing, or value-based partnerships. Financial projections play a crucial role in quantifying the return on investment.
Adopting a strategic, requirements-driven approach before diving into design and development establishes a solid foundation for healthcare applications that maximize clinical impact, user satisfaction and financial sustainability over the long term.

Having addressed strategic consideration, we now delve into the development cycle, which includes:
This includes conducting discovery workshops with stakeholders to align on objectives, scope, and requirements, as well as developing the project plan, timelines, milestones and governance model.
The phase focuses on research to define priority use cases and personas through surveys, interviews and other techniques. System architecture diagrams, technical specifications, data models and compliance requirements are outlined. The technology stack and development methodology are also selected during this phase.
This stage begins with low-fidelity wireframes, enabling the visualization of general layouts and flow. High-fidelity clickable prototypes are then created to simulate a realistic user experience. Usability testing is conducted by observing representative users, then feedback is incorporated into prototype revisions until designs are finalized.
The development team is organized into small, cross-functional Agile teams that each work on specific features. Iterative development and validation are accomplished through sprints lasting 1-2 weeks. Code implementation adheres to standards like HIPAA HL7 and modular architecture principles. Each component undergoes rigorous testing followed by validation.
Addressing compliance and security considerations is critical throughout the process. Initiatives like implementing authentication and encryption, integrating privacy-by-design principles, conducting risk assessments and penetration testing help embed compliance by design.
Before the product release, staging and production environments are established for testing. Releases are gradually rolled out to users while monitoring and gathering feedback. The post-launch stage involves maintenance such as managing bugs, releasing enhancements and updates, backups and providing support.
The phased approach enables alignment of requirements, prototyping of the design, iterative development, and the maintenance of a secure, compliant, and high-quality mobile healthcare application.
Building a healthcare application requires a deep understanding of both patient needs and technological considerations. By following key steps — from ideation to deployment and maintenance — developers can create a secure, user-friendly custom healthcare solution that meets the needs of both providers and patients. When built with a comprehensive understanding of all objectives, healthcare applications hold tremendous potential not only for business success but also for transforming lives by enhancing access, managing chronic conditions, and supporting a value-driven healthcare system. To truly make an impact, partnering with an experienced healthcare technology company is key. EffectiveSoft has over 20 years of expertise in building innovative healthcare solutions. By leveraging EffectiveSoft’s development capabilities and knowledge in the healthcare domain, your application can deliver maximum value to all stakeholders. Contact our team of experts today to discuss how we can bring your digital health vision to life.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form to receive a consultation and explore how we can assist you and your business.
What happens next?