
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

The Internet of Things is one of the most prominent technologies driving the progressive future. Along with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), augmented and virtual reality, blockchain, and other innovations, the IoT digitalizes society, making our lives easier and creating exciting possibilities. To better understand the current state of the IoT industry and how it’s going to change in the near future, let’s look at some statistics:


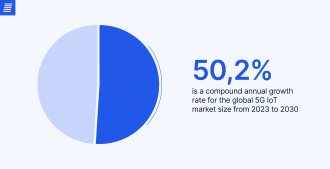

As statistics show, IoT technology is currently thriving, attracting users, and creating new opportunities for both personal and professional applications.
In this article, we’ll explore the latest IoT trends, from its diverse applications in various sectors to advancements in the technology itself, and examine how these IoT trends are transforming the world.
The IoT ecosystem integrates cloud computing, advanced data analytics, wireless networking technology, and a wide array of devices, from industrial machinery to household items. These devices use sensors to collect data from the outside environment. That data is then stored on the device, in the cloud, or at a network hub. Once collected, the data is processed, often using AI and ML.
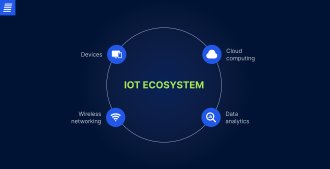

IoT devices use this processed data to undertake various actions. For instance, smart lighting systems can be programmed to switch on and off based on schedules, motion, or sound to prevent excessive energy use. Let’s examine the future trends in IoT to understand how the technology can change and improve our lives.
IoT and AI go hand in hand. This synergy is known as artificial intelligence of things (AIoT).
IoT devices gather information from the real world. Depending on the specific application, this data may be derived from movement, location, temperature, humidity, etc. The collected data is transmitted via IoT devices to a central system, typically a cloud-based platform, where it is processed and stored.
AI algorithms and ML models are then applied to analyze the collected data and extract insights. This may include predictive maintenance, pattern identification, anomaly detection, and other activities.
Thanks to the real-time processing capabilities of AIoT systems, intelligent decision-making systems can, for instance, trigger automated notifications or actions, such as adjusting a room’s temperature or notifying a user of an impending event.
One example of AIoT in the automotive industry is autonomous vehicles (AVs), which are equipped with numerous sensors that continuously gather large volumes of data on traffic conditions, including weather, terrain, routes, and more. The car’s navigation system uses AI models to turn this data into insights that allow it to perform complex real-time route planning.
AIoT can also manage energy consumption. Using properly placed IoT sensors and devices, businesses receive accurate insights into the energy use of major appliances like air conditioners, water heaters, refrigerators, and washing machines. These sensors collect and transmit data, giving users a thorough overview of energy usage patterns and enabling the implementation of optimization strategies.
Another area that can be significantly advanced through AIoT is video surveillance. Integrating ML algorithms into video feeds allows AIoT systems to analyze data in real time, detect objects, recognize people, and identify events automatically, thereby enhancing security at various facilities, such as stores, educational institutions, and entertainment centers.
According to a MarketsandMarkets report, the IoT security market will grow from $20.9 billion in 2023 to $59.2 billion by 2028, reflecting increasing security concerns. More IoT devices means more user data, and the more devices are linked to the Internet, the greater the risk that cybercriminals will exploit this data. Thus, in the upcoming years, security will be a crucial issue within IoT trends.
As security threats become increasingly serious, it’s imperative to ensure adequate protection. While basic security measures like changing default privacy settings, enabling multifactor authentication, setting up a secure firewall, and updating software are important, advanced IoT security measures can take your security to the next level.
One of these measures is the use of simple network management protocol (SNMP). SNMP monitors network devices and detects abnormal traffic patterns that indicate threats, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. By analyzing SNMP management information base (MIB) variables, the system categorizes traffic as either “normal” or “attack.” It also employs Kullback–Leibler divergence (KLD) to detect false data injection by comparing data distributions before and after network transmission.
Another IoT security strategy is network segmentation, where the IoT network is divided into separate sections, each equipped with its own access controls and security measures. This strategy mitigates the impact of attacks and helps prevent possible breaches. Segmentation enables the differentiation between internal user traffic and that of visitors and outside contacts, establishing separate segments for databases and web servers.
IoT has been transforming healthcare for many years, expanding its capabilities to wearables and connected medical devices, ranging from glucose and heart rate monitors to air quality sensors and lighting control in hospital wards. IoT devices excel at tracking and preventing chronic diseases, streamlining clinical workflow management, improving medication safety observation, and facilitating remote patient monitoring. The size of the healthcare IoT market is predicted to reach more than $446 billion in 2028, up from about $71 billion in 2020. Let’s look at some of the major trends in healthcare IoT.
One of the key IoT market trends in healthcare is telemedicine, which allows patients to receive medical care via the Internet without the need for an in-person visit or a conventional office environment. This model facilitates medical care for elderly people, people with mobility issues, rural residents, and others who may face barriers to accessing traditional healthcare services. It also helps prevent the spread of infectious illness, enables middle-of-the-night care, lowers medical costs, and reduces the load on hospitals.
IoT industry trends also include personalized medicine, which typically involves the identification of genetic predispositions to guide cancer therapy, prevent chronic illness, and treat allergies. Along with the data on a patient’s biological markers, genetic susceptibilities, and medical history, personalized medicine often entails utilizing data from wearable health devices for real-time health management and monitoring.
IoT is also valuable for hospital operation management, with real-time location systems (RTLS) being a prime example. These systems track the real-time movement of medical equipment, ensuring the efficient utilization of resources. Another case is environmental monitoring equipment, which tracks parameters like humidity, temperature, and air quality in operating rooms, hospital wards, medication storage areas, and other medical spaces. This not only ensures patient well-being but also ensures compliance with safety regulations.
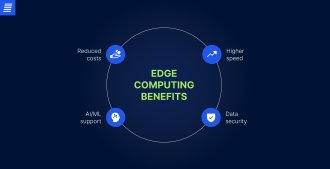
Typically, IoT applications send data from smart devices to a centralized cloud or data center for processing. However, network capabilities struggle to keep up with the increasing volumes of data. With edge computing, computing power and data storage are deployed closer to the devices that generate the data and their users. This improves IoT application performance in several ways:

According to Allied Market Research, the global IoT market size was about $28 billion in 2012 and was expected to reach $177.9 billion by 2023, representing a CAGR of 20.3%. This rapid growth is due in part to the successful integration of technology into the retail sector and the superior results that integration has delivered.
The IoT automates processes, provides advanced analytics, improves customer experience, reduces costs, and facilitates store management, among other things. Here are some of the prominent examples of IoT applications in the retail industry.
Smart shelf technology helps track the movement of items to and from the store, analyze the efficiency of ads, and improve the customer experience with the help of various solutions:
With self-checkout, customers scan product barcodes using mobile apps and pay online without interacting with staff. More advanced checkout solutions, like the one offered by Amazon, can read the tags on each item when a customer leaves the store and bill them instantly through smartphone apps. As a result, stores require fewer employees, and customers spend less time in a store, preventing overcrowding and frustration.
For some goods—including medications, plants, and fertilizers—methods of transportation and storage are particularly important. Failure to comply with the necessary conditions may result in product spoilage, leading to significant financial losses. To avoid damage, environmental sensors can be installed in delivery trucks, warehouses, and stores to track temperature, pressure, and humidity in the environment in real time, enabling early detection and the elimination of any issues.
5G was created with IoT applications in mind, including remote work, delivery robots, autonomous cars, connected drones, and public safety applications, among others. While many IoT applications are currently supported by 4G, bandwidth limitations can restrict their applicability to various IoT technologies. By leveraging unique radio frequencies and shorter wavelengths, 5G offers superior bandwidth, energy efficiency, and enhanced security features.
Blockchain is a type of decentralized digital database or ledger where the data is recorded across a network of computers, also known as nodes. The data is stored in a series of blocks linked via cryptography. Every transaction is captured as a single block of data, which contains transactional information, a unique hash, and a time stamp indicating the precise moment when it was mined or confirmed.
Each block also contains the hash of a previous one. Therefore, any modification to the data in a block alters its hash. An intentionally changed block would be rejected by the network because the hashes would not match. This inherent security feature makes blockchain a highly reliable system. Given its immutability, the blockchain is particularly well-suited for securely storing and authenticating data created by the IoT.
A digital twin is a virtual copy of a physical system or object, ranging from cars and cities to pipes and even human bodies. These digital models are used to simulate performance, identify issues, and conduct experiments to optimize real-world entities using data gathered by IoT sensors installed on real prototypes. Advantages of integrating digital twins with the IoT include:
Ongoing IoT industry growth has infiltrated various domains, enhancing them and creating opportunities for further advancements. Driven by growing needs, IoT technology has undergone significant performance enhancements, including integration with various solutions, including 5G, blockchain, AI, and more. Given its widespread adoption, it’s clear that IoT isn’t going anywhere, which means it’s time to consider using the technology in your business. Contact us to learn more about integrating the IoT with your organization’s current systems and equipment.

The IoT ecosystem integrates various kinds of devices. These gadgets gather information from the external world using sensors. The device, the cloud, or a network hub are the next locations where the data is kept. Once gathered, data is processed with the help of AI and ML. Later, these processed data can be used by IoT devices for a number of purposes.
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) is the term used to describe the symbiosis of IoT and AI. IoT devices collect data from external sources, and the data is then sent to a cloud-based central system, where it is processed and kept. The collected information is later analyzed using AI algorithms and ML models, and necessary insights are produced. AIoT can be applied in healthcare, agriculture, retail, energy management, environmental monitoring, and many other spheres.
For many years, the Internet of Things (IoT) has been revolutionizing the healthcare industry by bringing wearables and connected medical devices into its fold, increasing the accessibility of healthcare, assisting with hospital operation management, tracking and preventing chronic diseases, improving medication safety observation, and facilitating remote patient monitoring.
IoT is widely and successfully integrated into the retail sector. Among the benefits of IoT-empowered technologies like smart shelves, self-checkout, cold chain optimization, and others are process automation, advanced analytics, cost reduction, enhanced customer experience, and improved store management.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659