Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
Smart transport supported by the Internet of Things (IoT) is growing at a staggering rate. The automotive industry is absorbing the latest trends in telecommunications, computer technologies, programming, and machine learning to produce safer and more comfortable vehicles. Moreover, automobile manufacturers understand the potential of IoT and seek to capitalize on its benefits. Let’s take a look at how IoT is used in the automotive industry and what possibilities it opens up.
To better understand the concept of automotive IoT, we should first consider the nature of IoT. In short, the Internet of Things refers to interconnected devices that communicate with each other through the Internet with no human input. One application of IoT is for manufacturing machines; in this context, automotive IoT refers to integrating IoT technologies into automotive systems to create new solutions. When we envision the future, we often imagine smart cars that drive on their own, talk to their passengers, maintain themselves, and fly. Today, this is no longer a futuristic story but a reality. And in this reality, machines with IoT already have several key use cases.

IoT best use cases in the automotive industry
Solutions and technologies to connect vehicles are already widely available. In this section, we will consider some of the most important use cases.
First, automotive IoT has facilitated fleet management. Sensors (e.g. GPS sensors, OBD2) embedded in different components of the car register data about speed, location, idle time, fuel consumption, load, temperature, driver behavior, and so on. Then, this data is sent wirelessly to the gateway and the fleet management platform for analysis.
IoT solutions facilitate the work of fleet management operators in several ways. With IoT, it is possible to:
As a result of IoT, fleet management has become smarter, saving time by eliminating much of the manual work of traditional approaches.
Always-green traffic lights, available parking spaces, low risk of accidents, people with disabilities feeling safe on the road — all this seems utopian, doesn’t it? But it is already possible with IoT in cars.
Internet-enabled intelligent systems allow modern vehicles to communicate both with each other and with the outside world. In this sense, vehicles are connected to everything (V2X). Depending on the “interlocutor”, we can distinguish between the following patterns.

IoT-connected vehicles
Cars connect to each other and share relevant information (location, engine temperature, route, speed, etc.) in real time. If dangerous conditions occur in a vehicle, the drivers of nearby cars receive a warning so that they can take measures to prevent an accident.
Cars connect to the surrounding infrastructure (lane markings, toll booths, parking, etc.) and receive data about traffic light signals, parking space availability, and so on. For example, by connecting to traffic lights, cars can inform their drivers about the amount of time until the next green light.
Cars connect with vulnerable road users (pedestrians, cyclists, public transport passengers, and so on) and receive information about their proximity. Pedestrians, in turn, get notified about an approaching vehicle, its speed, direction, etc. Pedestrians can use this information to detect and predict the trajectory of vehicles at a particular time.
Cars and drivers interact via a mobile app. Using their smartphone, drivers can open and close the car, start and stop the engine, check the gas level or the battery level, park the car from outside, etc. Vehicle to Network (V2N) — Cars connect to mobile networks to exchange data with the cloud in real time.
IoT solutions are used to track vehicle parameters and notify the driver of potential failures of automotive systems. Today, all modern automobiles are equipped with wireless connections and sensors (including position and speed, air flow, exhaust emission control, temperature, pressure, and more). The system gathers the relevant data from the sensors and compares it with the preset limits for the vehicle type. In case of any discrepancy, the car alerts the driver.
In turn, connecting cars to the cloud enables the real-time synchronization of this data. In addition, car owners can use smartphones to view information about their vehicle and receive notifications through their online accounts.
This ability to identify and prevent breakdowns before they occur helps save time, money, and anxiety while improving overall road safety.
Modern in-vehicle infotainment is no longer an outdated push-button radio receiver but a whole system that connects to all smart car technologies, including ADAS, V2X connection solutions, sensors, etc. Some manufacturers develop their own software, while others integrate off-the-shelf Apple and Google products like CarPlay or Android Auto. Such products aid in navigation, play audio, enable hands-free calls, provide access to third-party apps like Skype and Spotify, and more.
There is one area where IoT in the automobile industry has already turned fiction into reality: autonomous vehicles, which represent one of today’s main automotive IoT trends.
Many people imagine self-driving cars as providing complete autonomy and a virtual robot driver whom they can talk to, but the fact is quite different. Indeed, autonomous cars are already widely used. However, they are not yet fully robotic cars that can move without human intervention.
According to one classification system, there are six levels of driving automation:
Level 0 (no automation) — The driver has to control everything.
Level 1 (hands-on) — The automated system acts as a driver assistant. Cars have adaptive cruise control, parking assist systems, and lane departure warning systems.
Level 2 (hands-off) — Cars are partially automated. Vehicles independently control the gas and brake, but the driver must always monitor the situation in order to immediately switch to manual control if necessary.
Level 3 (eyes-off) — This level is characterized as conditional automation. The car can drive on its own, but the autopilot is effective only in ideal road conditions. The driver should be ready to interfere at any time — for example, if there is a risk of an accident.
Level 4 (mind-off) — The level is defined as high driving automation. The car can do everything the Level 3 cars do but can also solve complex traffic situations. However, unmanned capabilities are not limitless yet. Examples of this level include Cruise and Google’s driverless taxis, which can only drive on the roads they have been trained on.
Level 5 (no drivers) — This is full driving automation. The car drives with no human intervention.
Among these levels, the most common are cars of levels 0–2. Cars at levels 3–4 are currently undergoing tests and are gradually entering the market. Meanwhile, vehicles of level 5 are still under development and do not transport passengers yet.
Studies suggest that autonomous cars will make the roads safer. Since most accidents are caused by the “human factor” (alcohol intoxication, fatigue, stress, etc.), it is logical to eliminate their main cause. Robotic cars can come to the rescue.
To move without drivers’ assistance, autonomous cars must be equipped with Artificial Intelligence to process the information from the sensors and cameras and to command the car. Furthermore, vehicles must be equipped with GPS, INS (Inertial Navigation System), and many other devices, including the following:
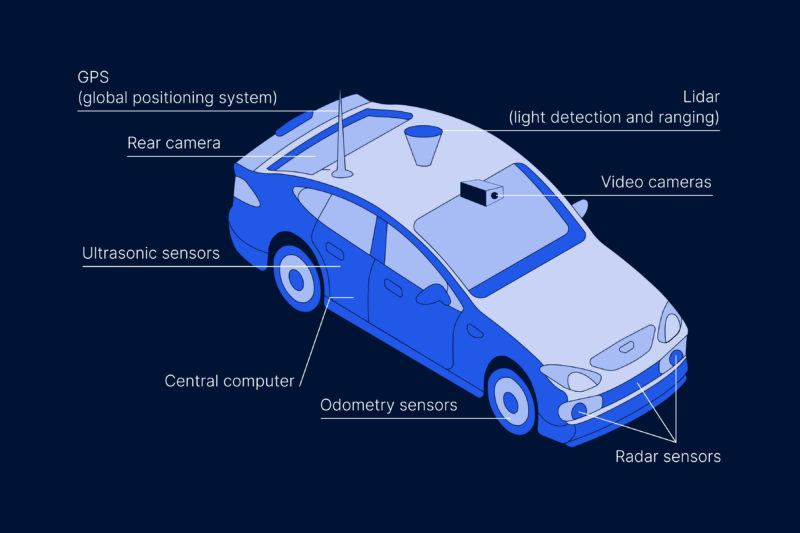
Internet of Things (IoT) components and sensors in vehicles
Developing software for the automotive industry is quite a challenging and long process. Before you start working on an app, you need to conduct a thorough market analysis in order to understand the current trends and assess the potential risks.
It is essential to analyze off-the-shelf solutions and evaluate all their pros and cons. Personally, we are always in favor of custom-built software. First, tailor-made solutions are created to meet the needs of a concrete client, so you can be sure that the app will fit you perfectly and work correctly alongside the car’s existing software and hardware. Second, made-to-order software is usually more cost-effective in the long run.
Once you have carried out the necessary technological and market research, you need to reflect on the app concept: how it will work, what specific purpose it is created for, who it is created for (drivers, businesses, passengers, etc.), and more. It is important to consider each of these aspects carefully while not forgetting the company’s resources.
To ease the process, you can turn to our top-notch Business Analysts, who will assess all the issues, risks, and advantages in order to provide you with the solution that suits you best. By entrusting the task to a specialist, you gain a huge benefit: you either save time and effort or can be sure you will get the trendiest app.
After the preliminary research has been done and a blueprint has been drawn up, the development team will get down to work.
Many developers can build an ordinary app for a car. But only the most skilled can develop an app that works well with the built-in systems, ensures hardware and software connectivity, and enables connections to third-party APIs.
At EffectiveSoft, we have gathered talented engineers who can handle a project of any complexity. Our experienced IoT software developers will be glad to help you find the solution that will lead you to the best possible outcome.
When developing automotive IoT solutions, developers must pay close attention to all the aspects of the system they build. This includes choosing the most appropriate tech stack.
There is a huge variety of IoT apps in the automotive industry. To choose the best languages and technologies to apply, it is mandatory to consider the software’s specifics. Therefore, we recommend approaching this question individually. Contact our software development company to learn which tech stack suits your app.
The app interface for cars should be as simple and clear as possible to avoid distracting the driver. Therefore, we suggest that you entrust this job to experienced UX designers to be sure your solution meets the requirements and offers a delightful user experience.
Security is one of the most challenging aspects of implementing IoT technologies in the automotive industry. Today’s car is no longer a stand-alone machine but one part of an entire ecosystem that encompasses smartphones, autonomous driving infrastructure, cloud services, and more. With poorly protected systems, cars can become dangerous weapons in the hands of cybercriminals. Security lapses can cost users data leakage, loss of control over the system, and even their lives.
When building a security system, engineers should approach the issue from the perspective of “how the system will react when an attack occurs”, not if. To protect all a system’s weaknesses, it is essential to calculate all the paths that cybercriminals will follow.
To ensure network and app security, several basic precautions must be taken:
Naturally, this is only a small part of what it takes to launch a secure app. Merely taking security measures is not enough; it is also crucial to thoroughly test the system. Our software QA services are perfectly suited for this task.
IoT software is becoming an integral part of modern machines. This is easily explained by the numerous advantages it offers: improved machine maintenance, a clear picture of the transportation process, road safety, an improved in-vehicle experience, and many more.
If you wish to build an automotive IoT app to keep up with the digital transformation in the automotive industry, drop us a line. Our experts will consult with you about the most efficient way to reap the benefits of automotive IoT.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form to receive a consultation and explore how we can assist you and your business.
What happens next?