Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

Have you ever imagined diving into a coral reef as a way to help physical rehabilitation? Or walking through your childhood neighborhood to help with memory recall therapy? VR, which immerses people in a 360-degree illusion of an artificial environment, transcended gaming long ago and is now bringing sci-fi concepts to real life. This article explores the significant impact of virtual reality in healthcare, including its applications, benefits, and limitations.
In 2024, the VR healthcare market is valued at just over $4 billion worldwide and is projected to reach over $13 billion by 2029, growing at a compound annual rate of 27.3%. This potential growth is driven by factors such as advancements in VR technology, its increasing adoption by medical professionals, and rising demand for innovative treatment options. As a result, 80% of clinicians believe that VR will have a significant impact on healthcare in the next five years.
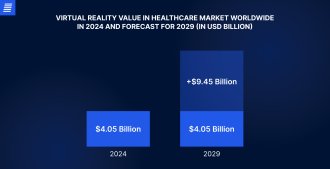

Source: statista.com
Although medical VR is a relatively new field, healthcare professionals have already explored and applied this next-generation technology in a number of cases, resulting in significant advancements. Here are the primary examples.
Unlike in a video game where you can restart a level after failing, doctors do not have a second chance to replay a situation if something goes wrong.
Fortunately, VR solutions facilitate total immersion in completely new environments where boundaries do not exist. This allows novices to acquire practical mastery alongside theoretical knowledge and enables seasoned doctors to repeat experiences and sharpen professional skills without fear of harming a patient. In addition, the virtual environment allows them to experience an unlimited number of scenarios they might encounter in their practice.
Leading medical schools and hospitals, such as George Washington University, are already leveraging VR to examine the anatomy of the human body, conduct surgical training, observe what happens during different physiological processes, practice different scenarios (e.g., resuscitation), and much more.
Medical imaging revolutionized medicine, providing doctors and scientists with visibility into the processes inside biological systems, particularly within the human body. This discovery also enabled caregivers to diagnose tumors, fractures, vascular diseases, or other abnormalities before symptoms appear.
VR moves medical imaging further, allowing for detailed 3-D visualization of organs, tissues, and bones. This helps doctors understand complex spatial relationships within the body, which is particularly beneficial in planning surgeries or treatments.
VR also enables clinicians to examine medical images from any angle and zoom in to see specific areas of interest. This can improve diagnostic accuracy, allowing for earlier detection of abnormalities and more effective monitoring of disease progression.
VR tools are particularly effective in the rehabilitation process for patients recovering from musculoskeletal disorders, traumatic brain injuries, stroke, cerebral palsy (CP), and other conditions. VR can recreate real-life activities, helping patients regain strength and coordination. For example, some children with CP cannot hold an object with their hands. The brain’s plasticity, along with VR technology, allows physicians to outsmart nature by forming new associative connections and enabling other parts of the brain to take over the impaired function. Under the supervision of a doctor, the child can reach and grasp objects in the virtual environment. The brain memorizes these movements and gradually develops motor capacity. In this way, VR not only offers the child an active learning experience but also engages them with an interesting game and boosts motivation.
Amputees often feel pain in a limb that is no longer there because the brain continues to anticipate movement and sensory feedback from that area. This type of pain is believed to be caused by a mismatch between expected and actual feedback during movement.
Advanced VR solutions can help patients suffering from phantom pain by simulating the missing limb. With VR headsets and motion sensors, patients play a computer game, using their limbs to navigate a virtual world. Motion sensors track the movement of their residual limbs to create and control the missing limb. The premotor cortex uses the realistic image of the missing limb generated by the medical software and gives the patients the “feeling” of the amputated limb, thereby tricking the brain and reducing the pain caused by the mismatch.
VR technology can be used for chronic pain relief, reducing opioid use that carries serious dependency risks. VR methods often incorporate the cognitive behavioral therapy method, but unlike the latter, can be used at home. VR offers a multisensory experience that engages patients on a deep level and helps them feel good. Patients don headsets and immerse themselves in artificial environments, which distract them from pain and build a foundation for pain relief.
VR can have dramatic results in treating various mental health conditions, including phobias, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and depression. It’s important to note that VR doesn’t replace traditional methods, but rather complements them.
VR’s ability to transport individuals outside the physical world into more controlled immersive environments helps individuals reduce fears, improve confidence, reflect on past situations, and more. A VR simulation can help individuals gradually become accustomed to the object of their fear and realize that it poses no threat. For example, a person traumatized by a car crash can safely experience public streets in the VR environment to confront their fear of traffic.
Above, we have highlighted several key applications of virtual reality in medicine that underscore its major benefits for patients and providers. In this section, we detail the advantages VR offers for the healthcare industry.
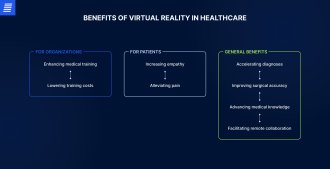

Above, we have highlighted several key applications of virtual reality in medicine that underscore its major benefits for patients and providers. In this section, we detail the advantages VR offers for the healthcare industry.

We leverage VR and wearable technology to provide DVR patients with accessible care.
With all its benefits and almost limitless possibilities, VR technology has yet to be widely adopted due to several significant challenges that must be addressed. Among them are:
Looking ahead, the future of VR in healthcare industry seems to be bright and full of possibilities. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect more innovative use cases that will enhance medical training, improve patient care, and foster better communication and empathy between healthcare professionals and patients.
One of the most promising applications of VR is telemedicine. The integration of this technology can assist medical organizations in addressing numerous telehealth challenges. It can be used to conduct seamless virtual meetings, interactive workshops, and immersive brainstorming sessions, allowing clinicians from remote locations to collaborate while examining patients’ records as if they were all in one place. When combined with AI-powered computer vision for visual analysis and identification, these technologies can elevate virtual healthcare communication and surpass those of standard in-person appointments.
By incorporating tactile sensations, haptic devices can provide realistic simulations for medical training and patient treatment. Surgeons can practice complex procedures in a virtual environment, feeling the resistance of tissues and organs as they would in a real surgery.
For patients, haptic feedback can be used in physical therapy, allowing them to interact with virtual objects and receive immediate sensory feedback, making rehabilitation more effective and engaging.
In combination, IoT, AI, and VR have the potential to create an interconnected, intelligent, and immersive ecosystem where data flows seamlessly between patients and providers, AI delivers insights that drive better care, and VR offers innovative solutions for both medical training and patient treatment.
Virtual reality is poised to transform healthcare by offering innovative solutions for training, treatment, and patient care. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and increasing adoption signal a bright future for VR in the medical field.
Embracing this technology can lead to more efficient, effective, and compassionate healthcare delivery; better-prepared physicians and surgeons; and more accurate diagnoses. All this can ultimately improve outcomes for patients worldwide.
Want to be at the forefront of VR healthcare innovation? Reach out to us and let’s make an impact together!

VR creates a fully immersive digital environment that replaces the real world, allowing users to interact with a completely virtual space. Augmented reality (AR), on the other hand, overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their actual surroundings without completely replacing them.
Yes, VR can be used to learn about individual medical conditions, treatment options, and possible outcomes in an understandable and realistic manner. Patients can virtually experience medical procedures before undergoing them, thereby reducing anxiety. Additionally, VR can educate patients with chronic diseases about their condition in detail, including showing what happens in their bodies, thereby inspiring people to take a more active role in managing their health.
Yes, we have successfully completed several projects dedicated to the development of VR-powered solutions for various industries, including healthcare.
Yes, there are risks associated with VR technology in healthcare. Some users may experience side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and eyestrain, commonly referred to as “cybersickness.” Prolonged use of VR can also lead to discomfort or disorientation. Additionally, there are concerns about VR’s long-term impact on mental health and the potential for overreliance on virtual simulations at the expense of real-world clinical experience. Ensuring proper usage guidelines and monitoring can help mitigate these risks.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659